by Conrad.

As this LiDAR image shows, the western portion of Blue Star Farm, run by Sue Decker, is located in Stuyvesant NY on terrace land above the Hudson River (seen on the left). A seasonal waterway drains north out of this farm, joining up with Mill Creek shortly before entering the Hudson. Sue’s “home farm” is slightly farther east along route 26A.
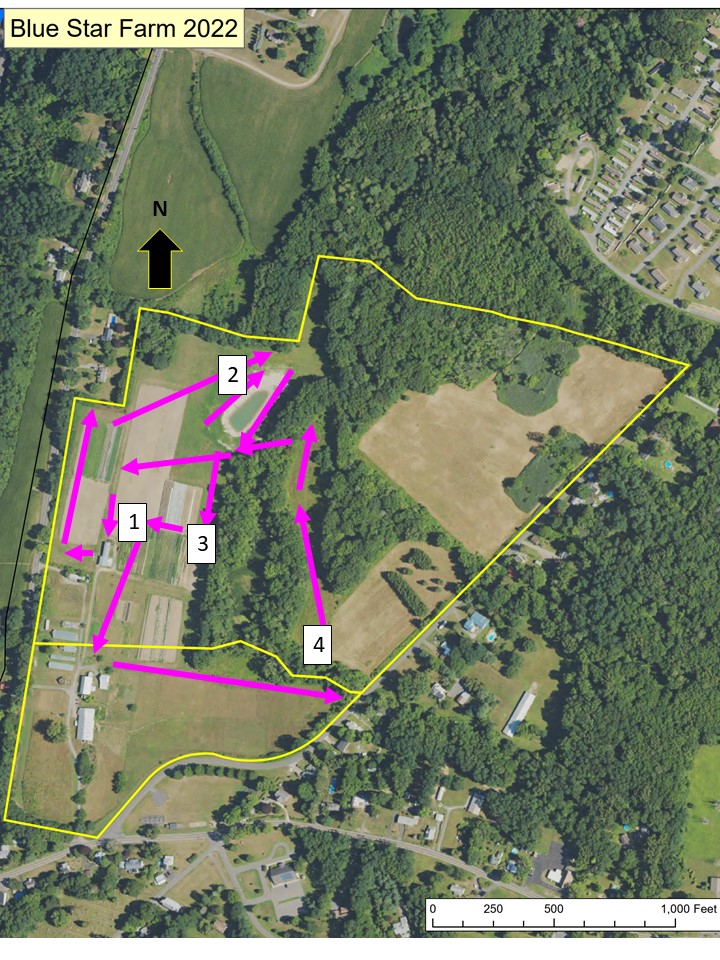
We parked just southwest of the “1” on the map and then headed north along veggie and cover crop beds, before cutting northeast to the new pond (near “2”) and then following the forest edge south, before cutting west through veggie plots to flower beds of Damsel Garden, run by land owner Denise Pizzini. We then moved south before turning east along the pastures, and finally bearing north into a finger of wettish meadow. The forested sections in the center of the land are wetland, sporting some interesting trees that Claudia will describe in a subsequent plant post.

In the 1940s, much of the now-forested area was cleared, although a patch of mature swamp forest existed near the center of the parcel. As was typical of this era, orchards were extensive, although they only nudged into the edges of the current farmland

This photograph looks north from near the point marked “1” on the earlier image.
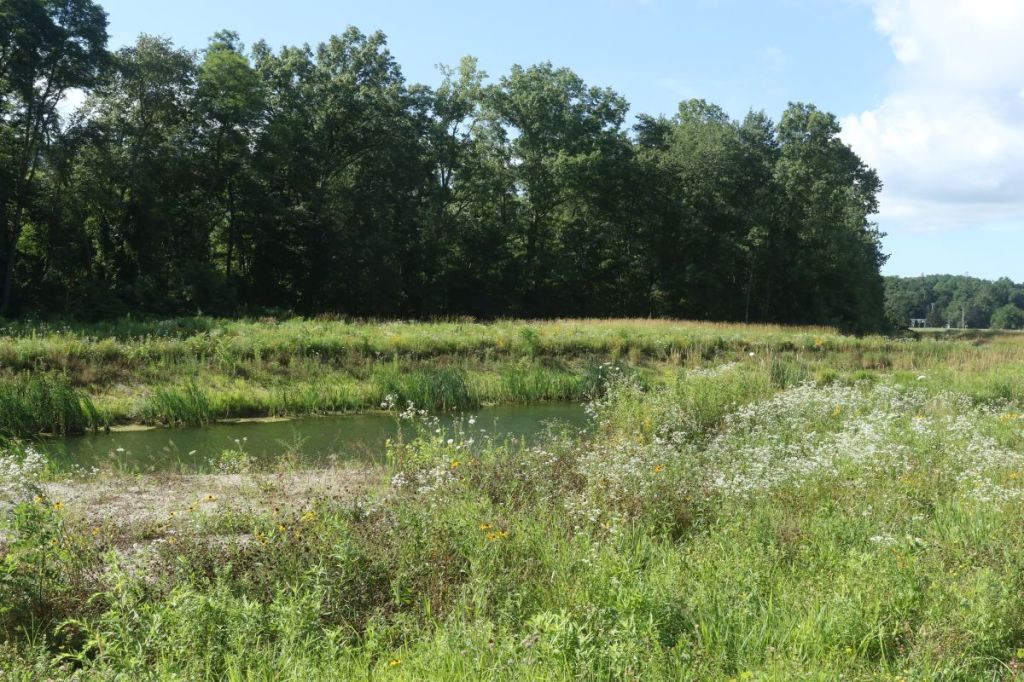

This photograph was taken from near point “2” and looks south, across a pond constructed around 2022. This was a dragonfly hot bed, as we’ll see later.
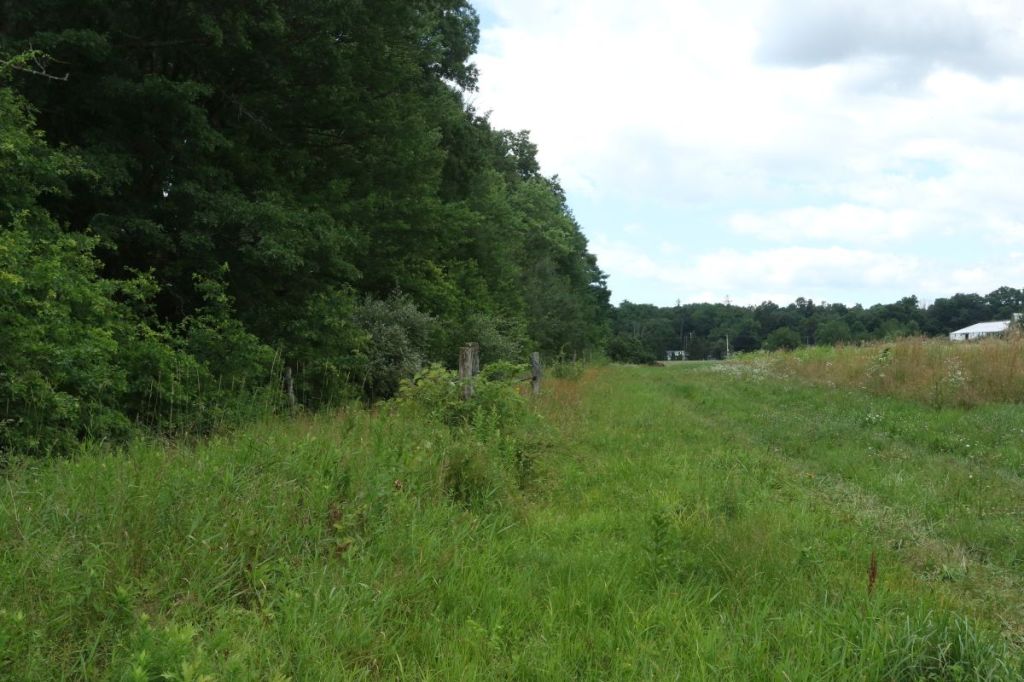

This picture, taken looking south from a bit north of point “3”, shows the welcoming (at least to insects!) soft edge with the forest.

This photograph was taken around point “3” and looks southwest across Blue Star veggie beds towards the buildings and beds of Damsel Gardens.
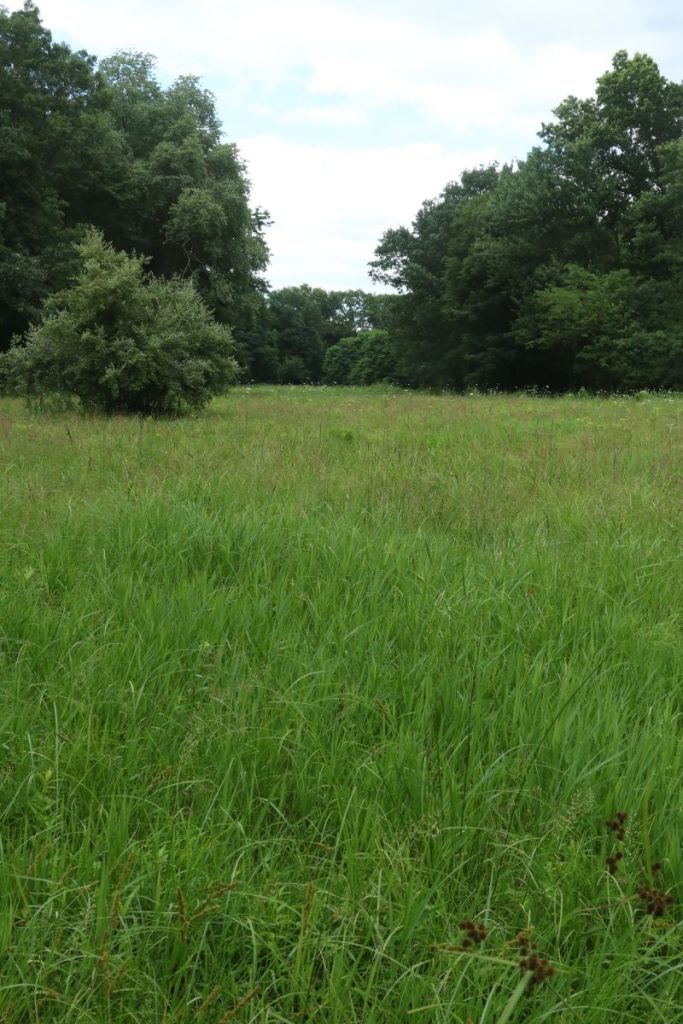

This wet meadow was photographed looking north from around point “4”. The mature swamp forest mentioned earlier is on the right.

One characteristic of this farm is its sandy soils, as evidenced here. These are remnants of Glacial Lake Albany beaches (or shallow, submerged sand flats). Making a cameo is one of the numerous grasshoppers we encountered. Most of the time they flushed hurriedly from in front of us, their large wings sometimes fooling us into mistaking them for short-flighted butterflies.

One consequence of the sandy soils seems to be ample habitat for native, ground-nesting bees, such as this Eastern Miner Bee (or close relative).

This graph illustrates data we collected from 19 Columbia County farms back in 2010. In and around tomato beds, we indexed flower abundance (much of which was unplanted “weeds”) and surveyed bees using bowl traps. This graphic shows that, relative to all other farms and especially for those with such low flower abundance, bees were very abundant at the current Blue Star site. Our guess was that this was because the sandy soil made excellent habitat for ground nesting bees. Bee diversity also appeared to be relatively high, ranking fourth in a quick and dirty assessment of diversity. We did not assess flower abundance during our current visit and it may well now be higher.

This native bee may be another species of mining bee.

Many bumble bees are also ground nesters.
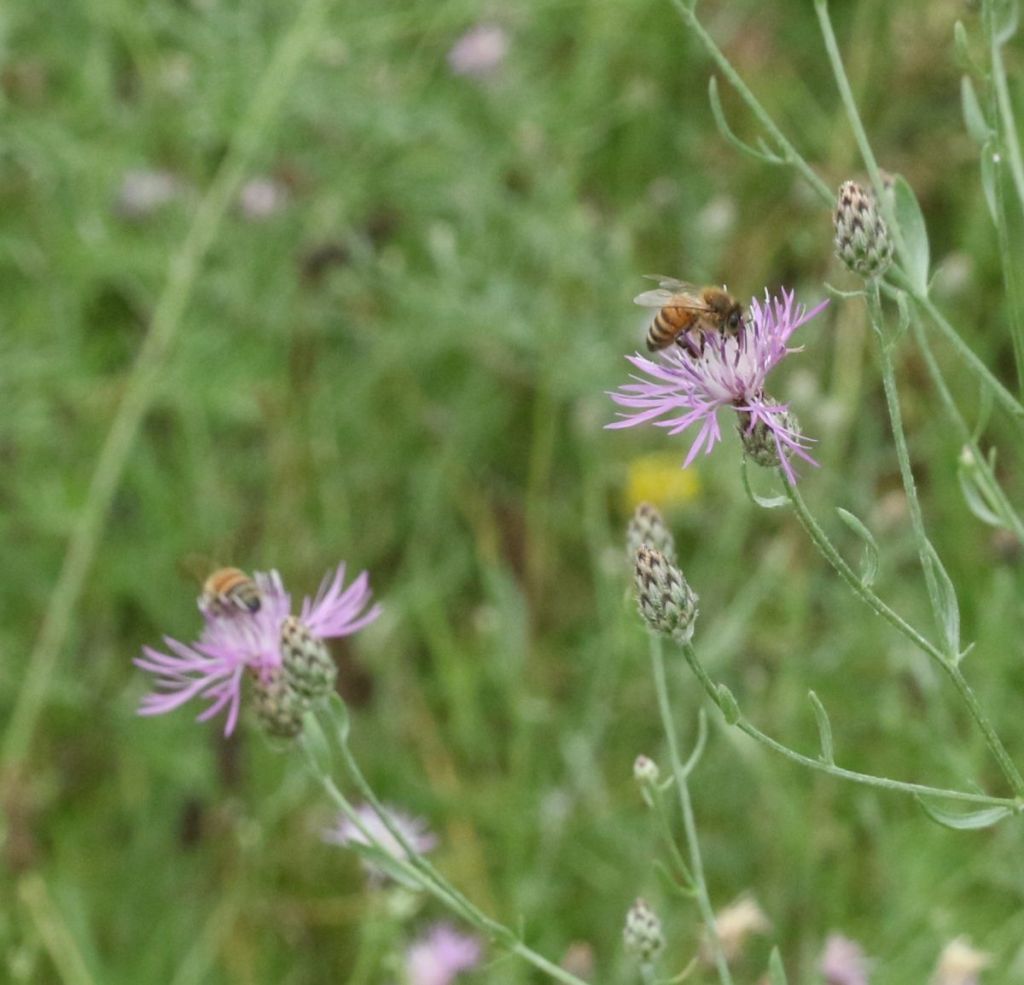

The most common bee species observed was the Honey Bee, likely originating from…
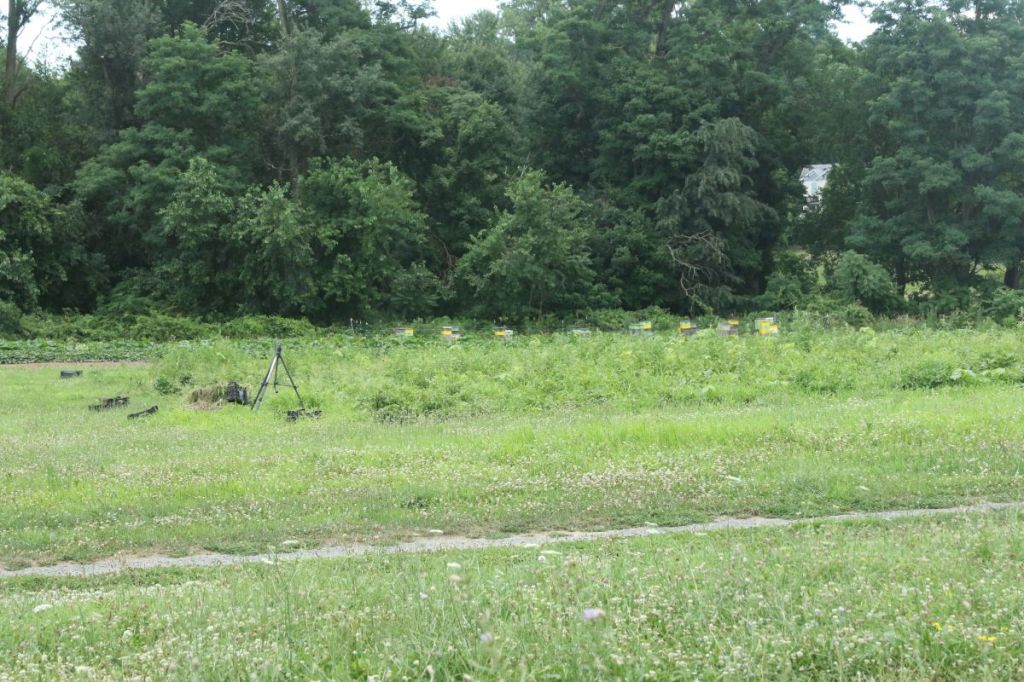

these hives along the forest edge. While many of us appreciate the honey, and Honey Bees can definitely be a boon to crop pollination, there is evidence that, at least under certain conditions, they can out compete native bees, thereby reducing the habitat quality for some species. Where native bees are abundant, additional pollinators are usually not needed.
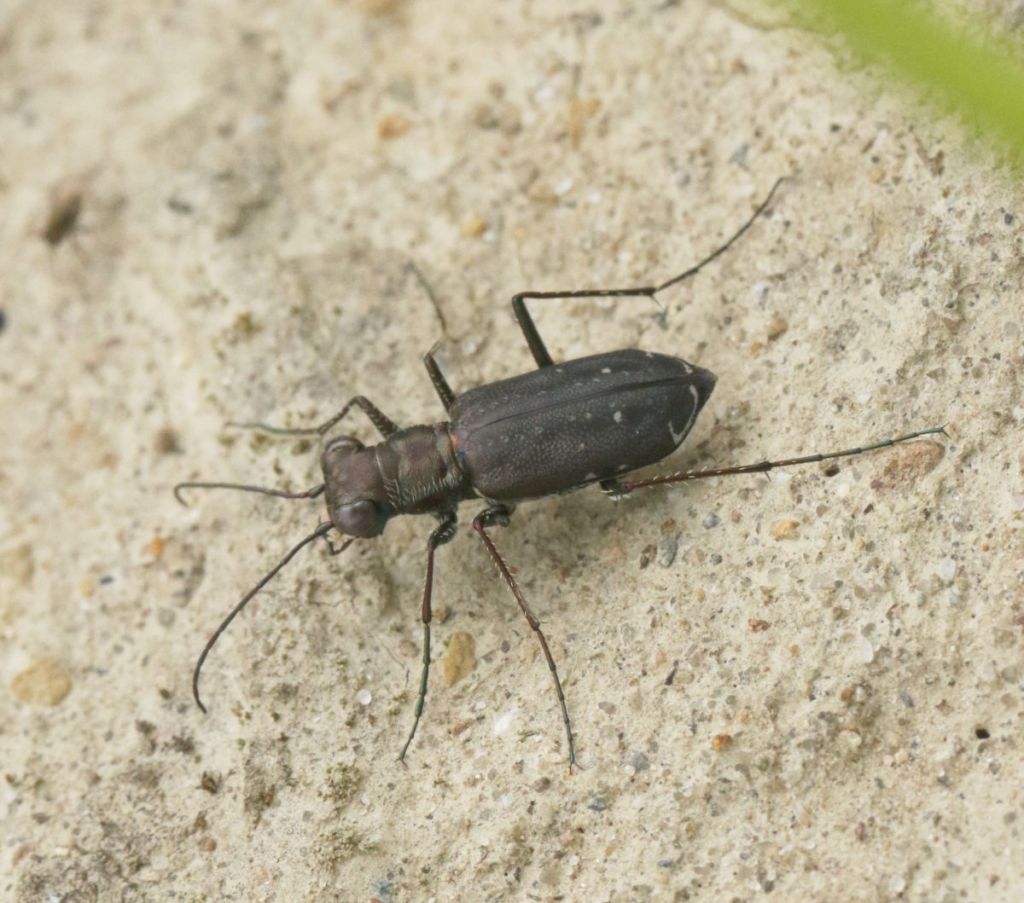

Open sand or clay patches are also favored by tiger beetles. This happens to be a “Punctured Tiger Beetle”, named for the row of point-like indentations along its back.
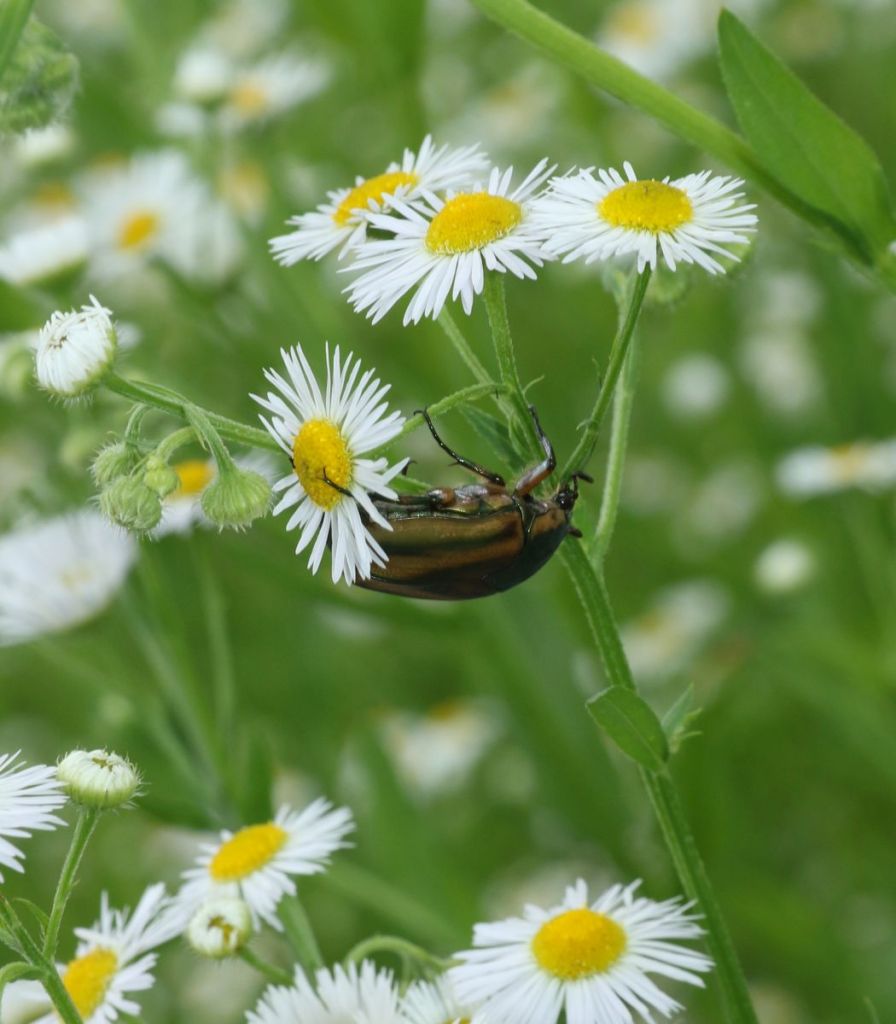

Speaking of beetles, this is a Green June Beetle, an elegant beetle with a wide-ranging diet, who is sometimes considered a minor agricultural pest.

Most of our attention was focused on dragonflies (& damselflies) and butterflies. We’ll start with the former.
This large dragonfly was seen flying over the aforementioned pond. While the green body and reddish tail could suggest a female Common Green Darner (a species that was also present), the brightness of the red, coupled with an evident white patch below the hind wings (not so evident in this photo, but clearer in others), suggests Comet Darner. Comet Darners are the biggest dragonflies regionally, and they are generally considered rare. We know them from only two other sites in the County.
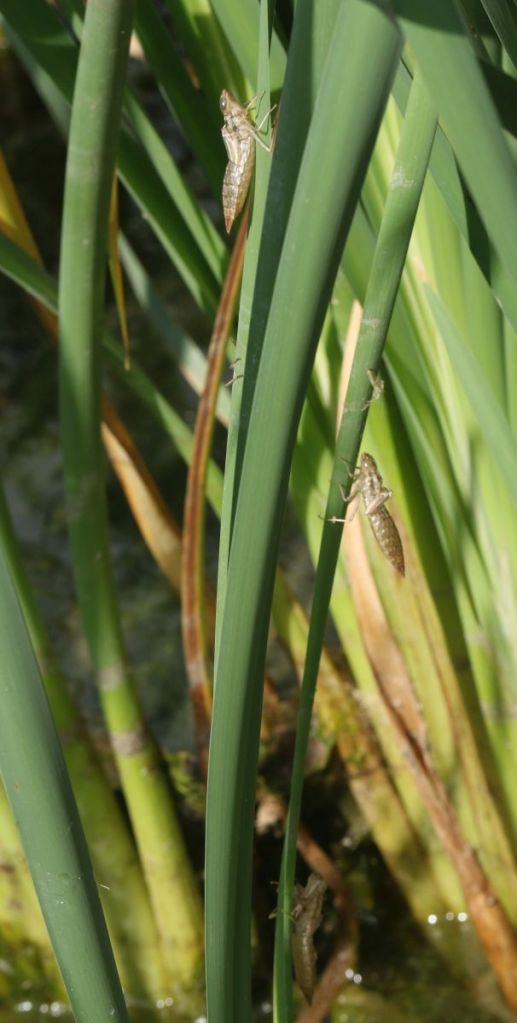

The vegetation around the pond edge sported numerous darner exuvia – the hollow, dry skins left behind when the aquatic nymph clambers out of the water, unzips its diving suit, and flies away. These appear to be exuvia of the Common Green Darner.
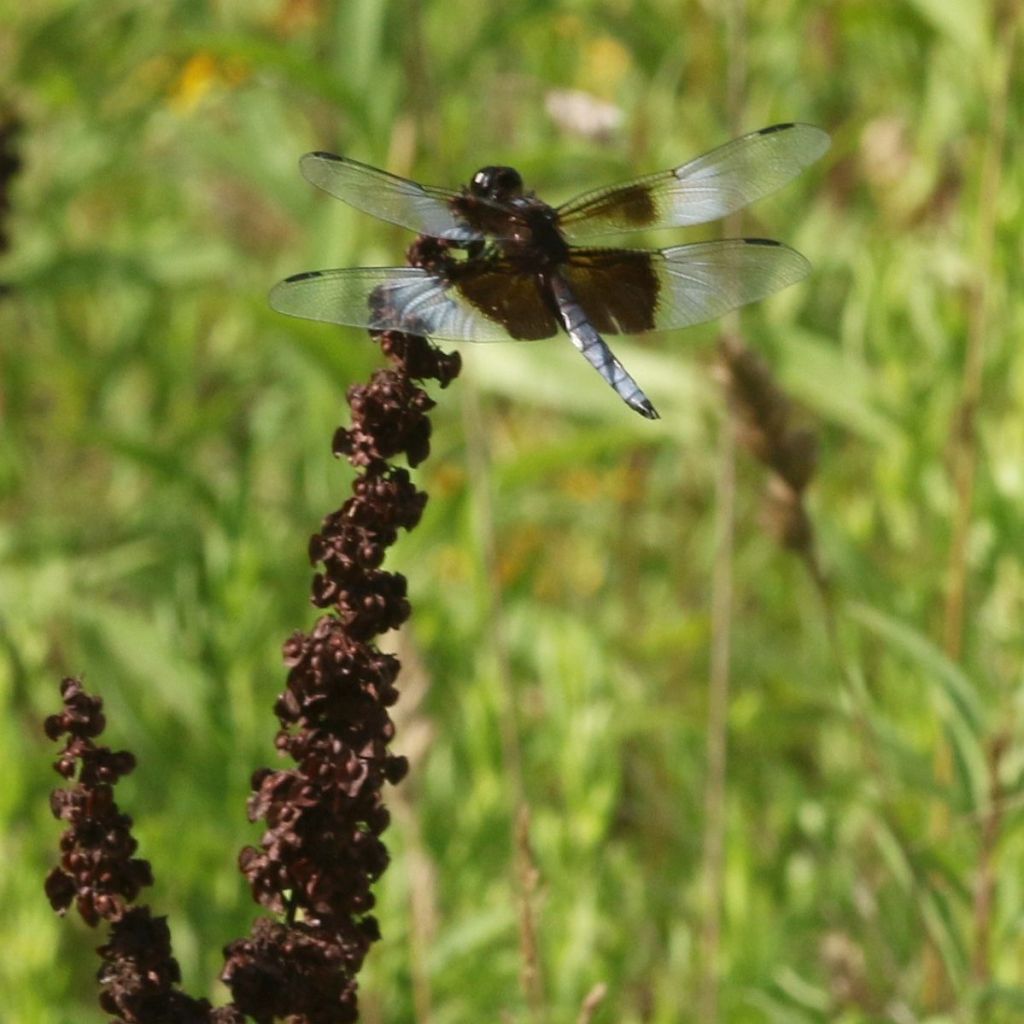

Widow Skimmers are common pond dragonflies that range widely in search of prey.
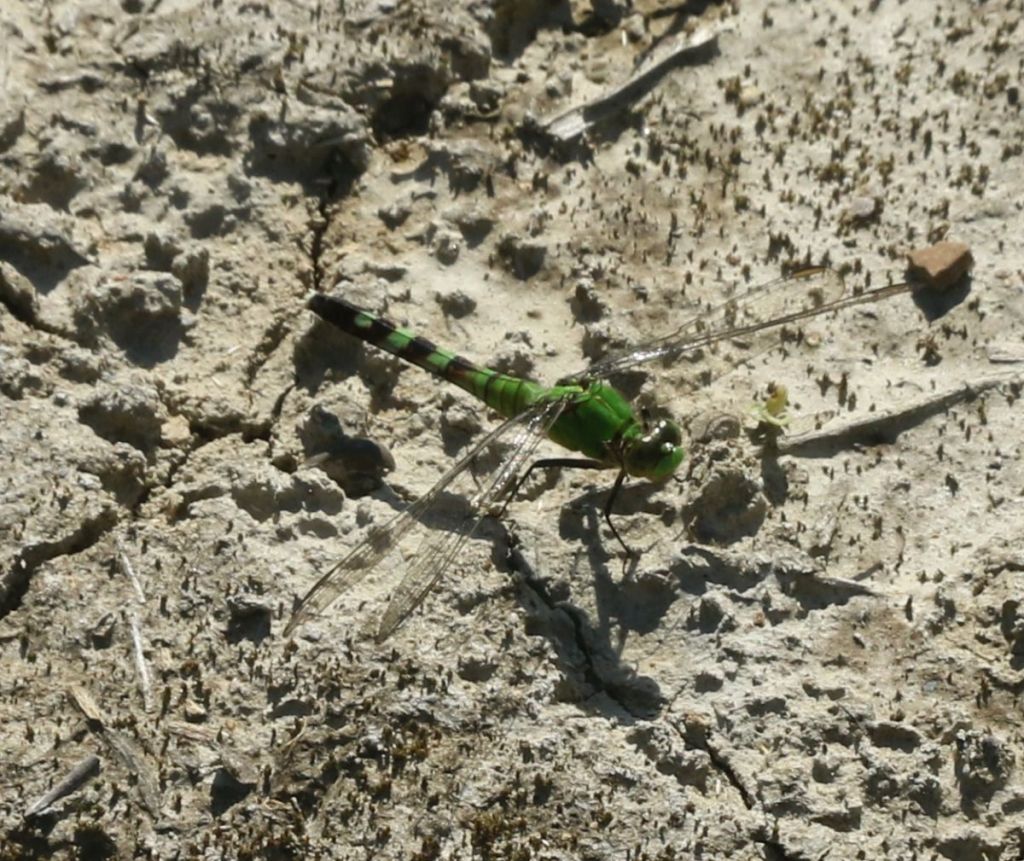

The Eastern Pond Hawk is another relatively common pond dragonfly. This bright green individual is the female, who has a much more verdant coloration than…
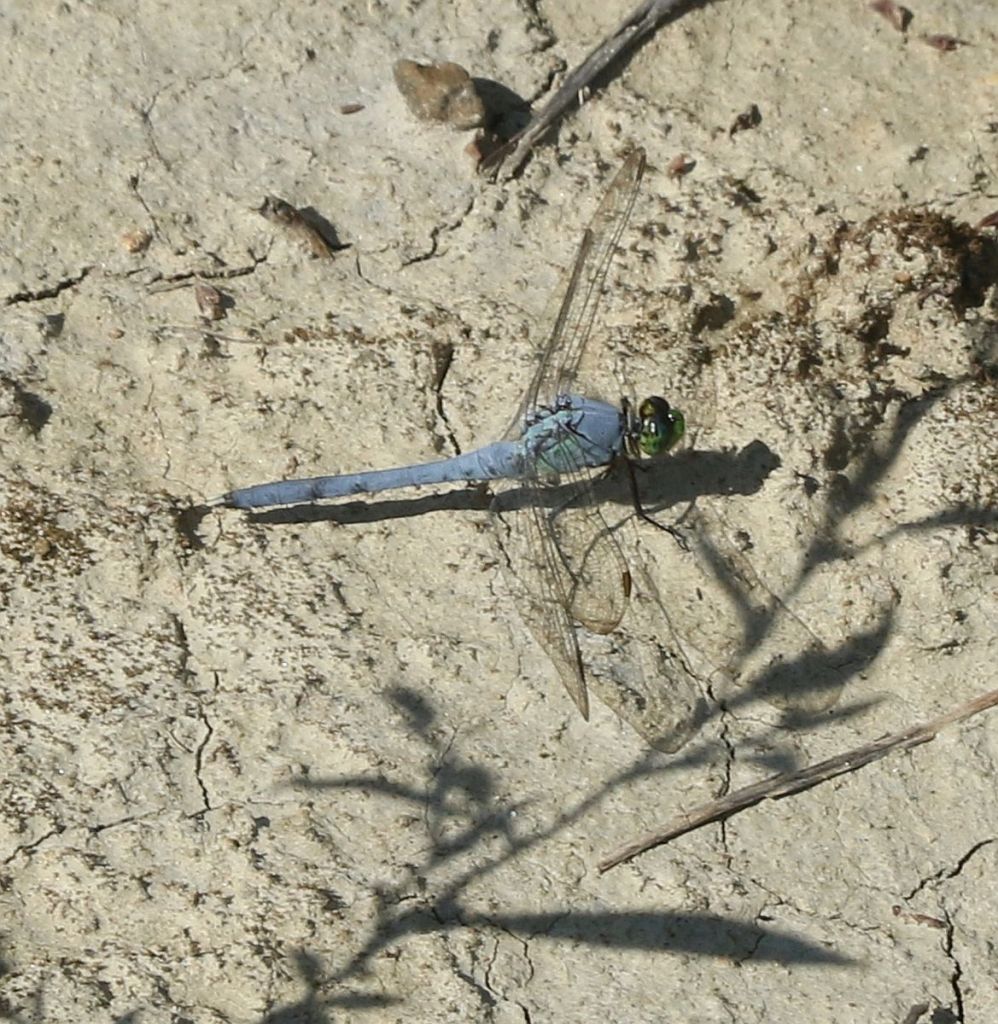

the blueish male shown above. One wonders if she is also more apt to hang out in green vegetation. As the traces of green suggest, the coloration of younger males resembles that of the female in many dragonfly species .
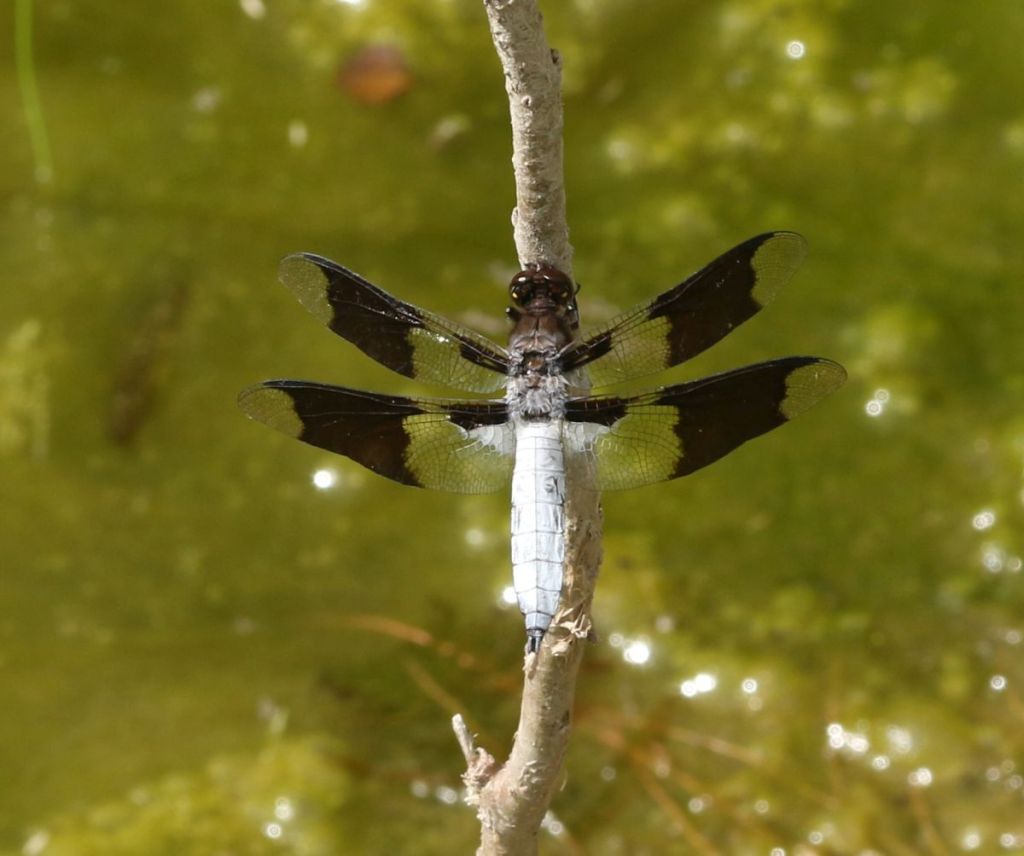

The name “Common Whitetail” almost says it all, but only the males have such white abdomens.

This slightly tattered Blue Dasher female also seems to carry its habitat’s design onto its thorax.
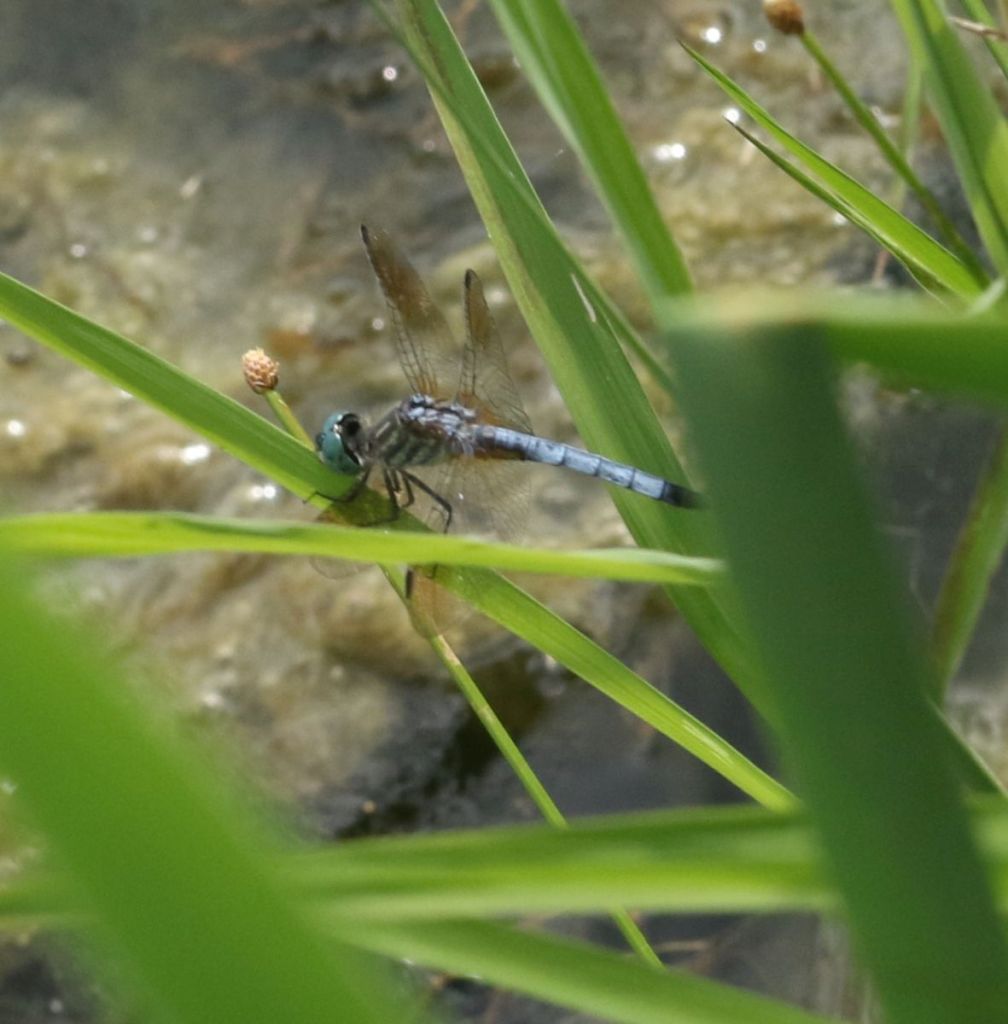

The Blue Dasher male tends to have a blue tail with a black tip.
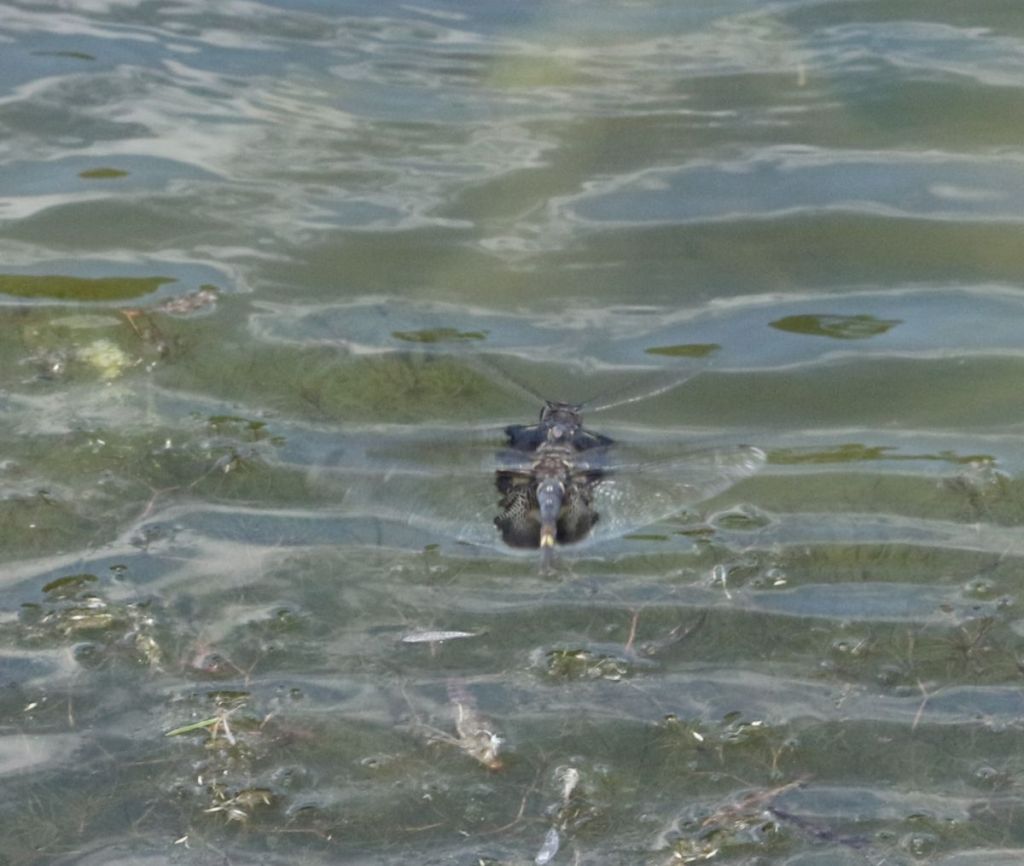

OK, I admit this is an odd angle. It shows a pair of flying Black Saddlebags from the back. The male is in front and is clasping the female behind the head with his aptly named “claspers”. Unlike Widow Skimmers, Pondhawks, and Blue Dashers, Black Saddlebags rarely perch. Rather than ‘hawking’ after prey from stationary resting points, this species does most of its hunting on the wing. This mated pair is probably not hunting, but rather looking for a place where their eggs can be deposited.
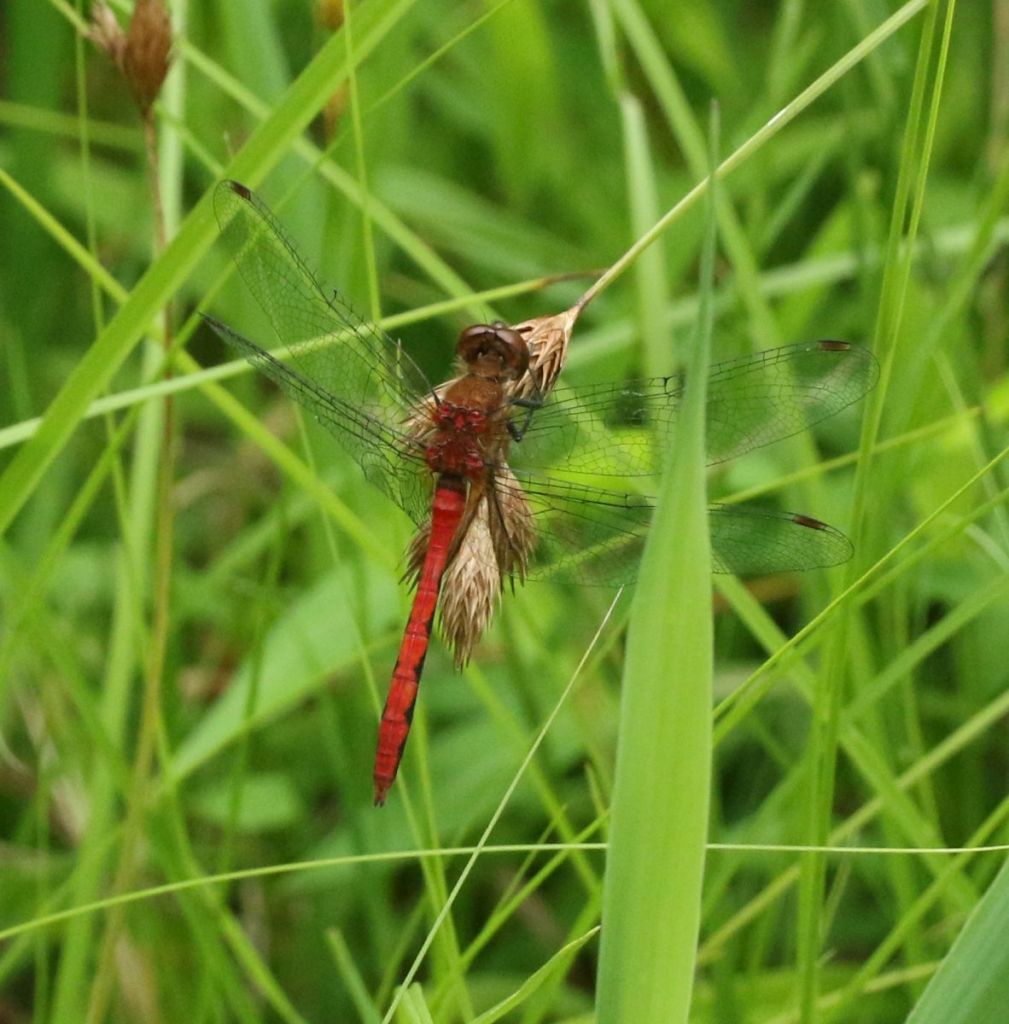

A mature male of one of our red-colored Meadowhawks. We have a trio of similar species and, not having tried to catch and inspect this individual more closely, I won’t guess at a species name.
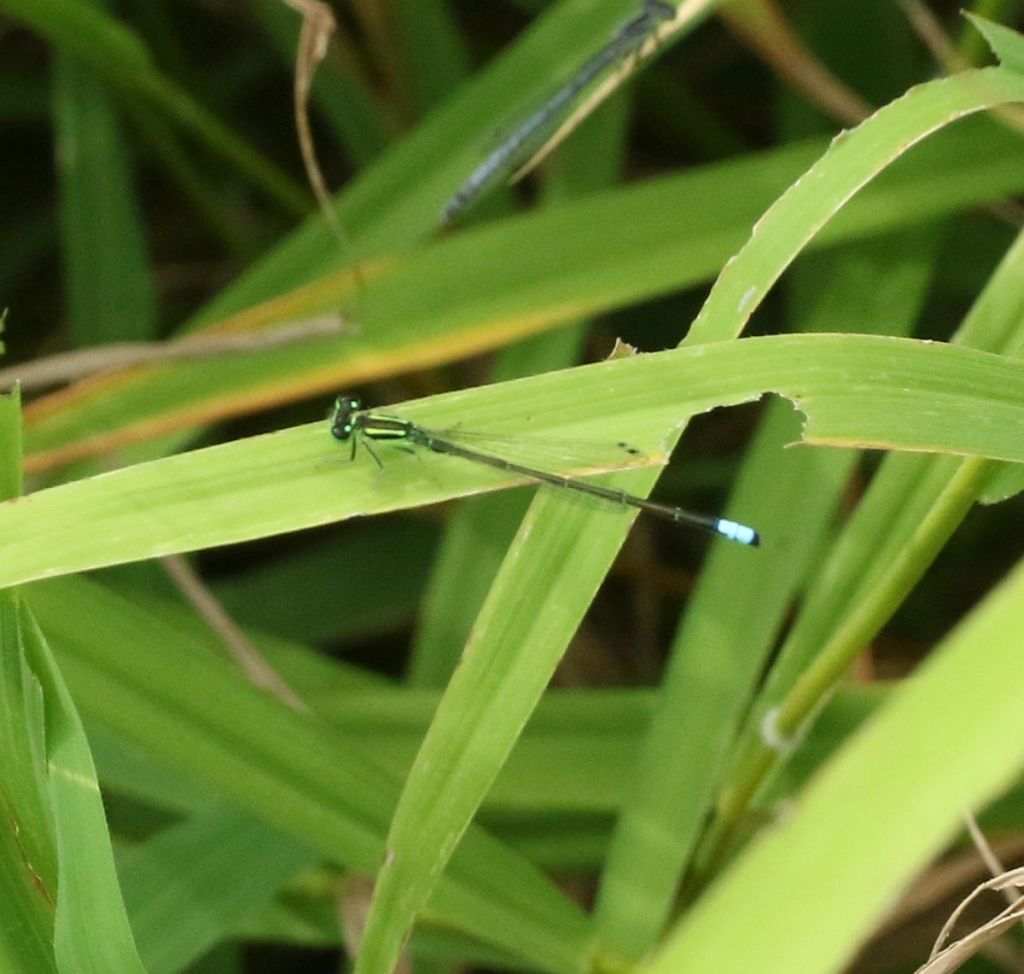

Damselflies are close relatives of the dragonflies, but are generally smaller, slimmer and hold their wings above their backs when perched. This damselfly is an Eastern Forktail, a common if somewhat inconspicuous species.
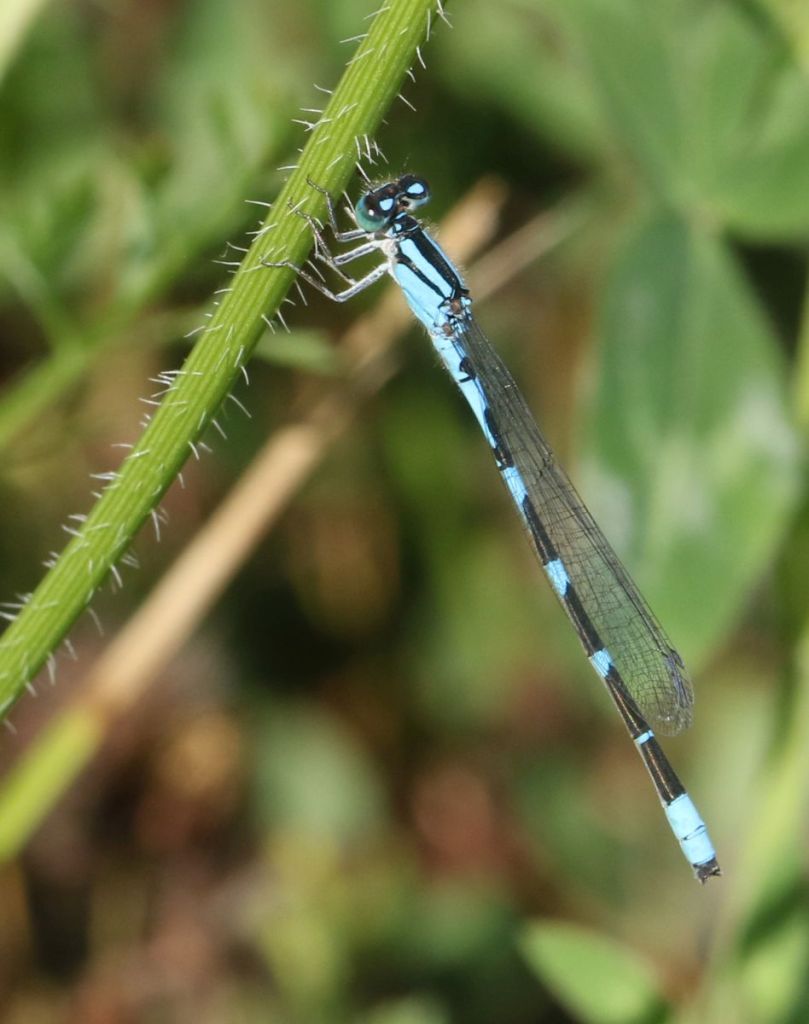

A Familiar Bluet. The defining characteristic for many damselflies and dragonflies is often those male claspers mentioned earlier; they are found at the very tip of the tail. Probably because they are an important component of the pairing process, their shape tends to be species-specific.

Damselflies can have exuvia too!
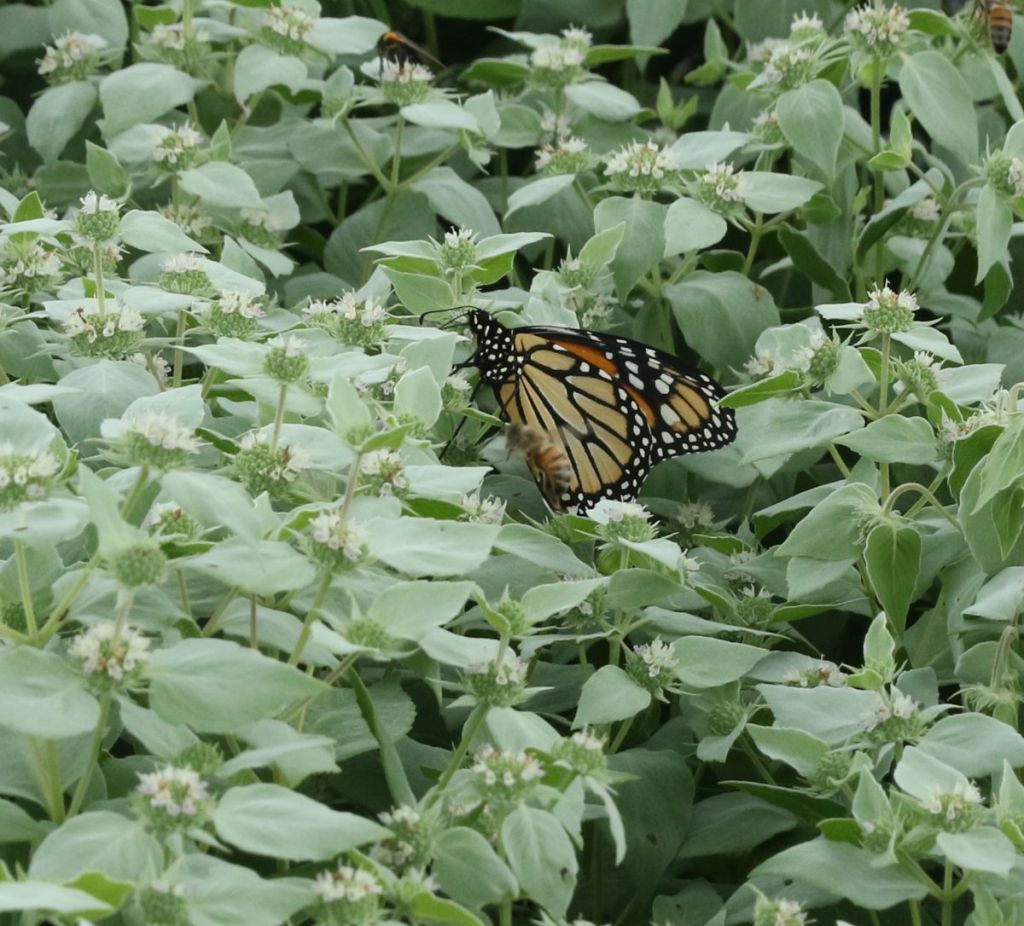

Moving on to butterflies, this is the iconic Monarch. We have seen a scattering of them so far this year.
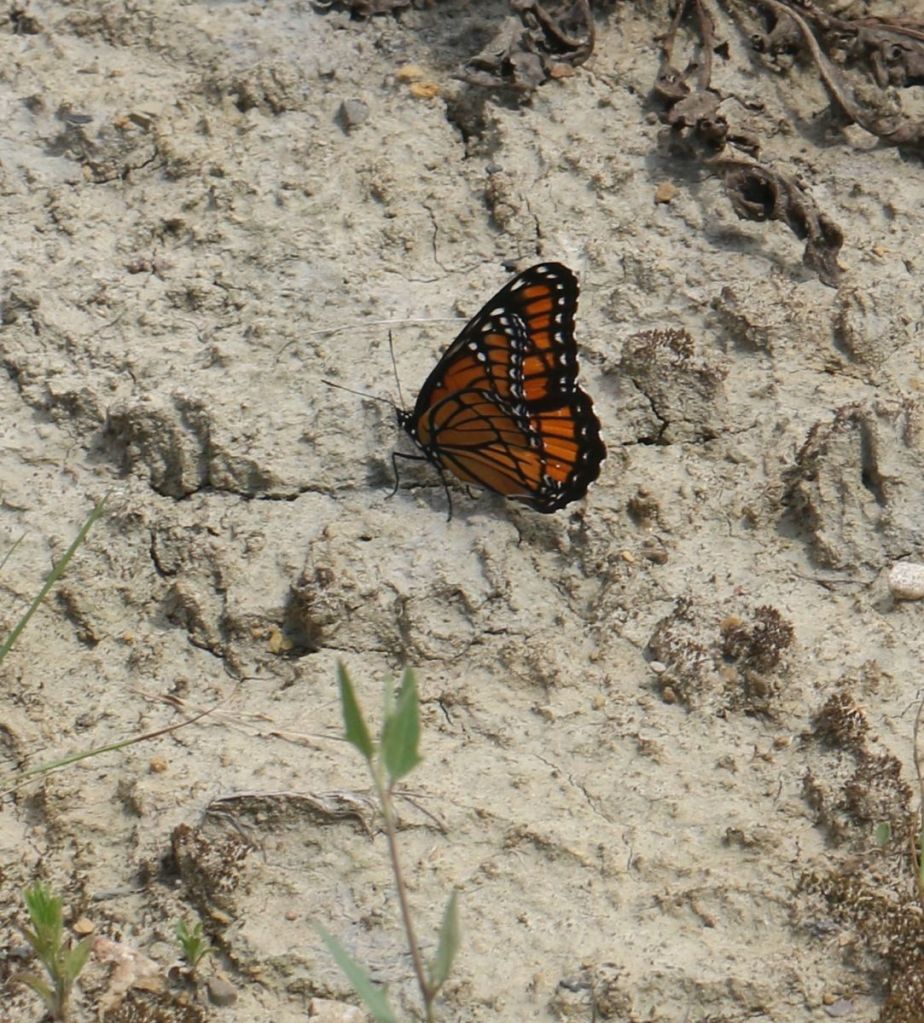

This is the Viceroy, a Monarch look-alike. It is usually smaller than a Monarch and has that distinctive black line paralleling the trailing edge of the hindwing.

Cabbage Whites were abundant at the farm. As hinted at here, their caterpillars (aka cabbageworms) feed on brassicas and can sometimes be crop pests. Cabbage White are not native, and were first noticed around the ports of Quebec City and New York in the 1860s, probably having hitched a ride on imported cabbages.
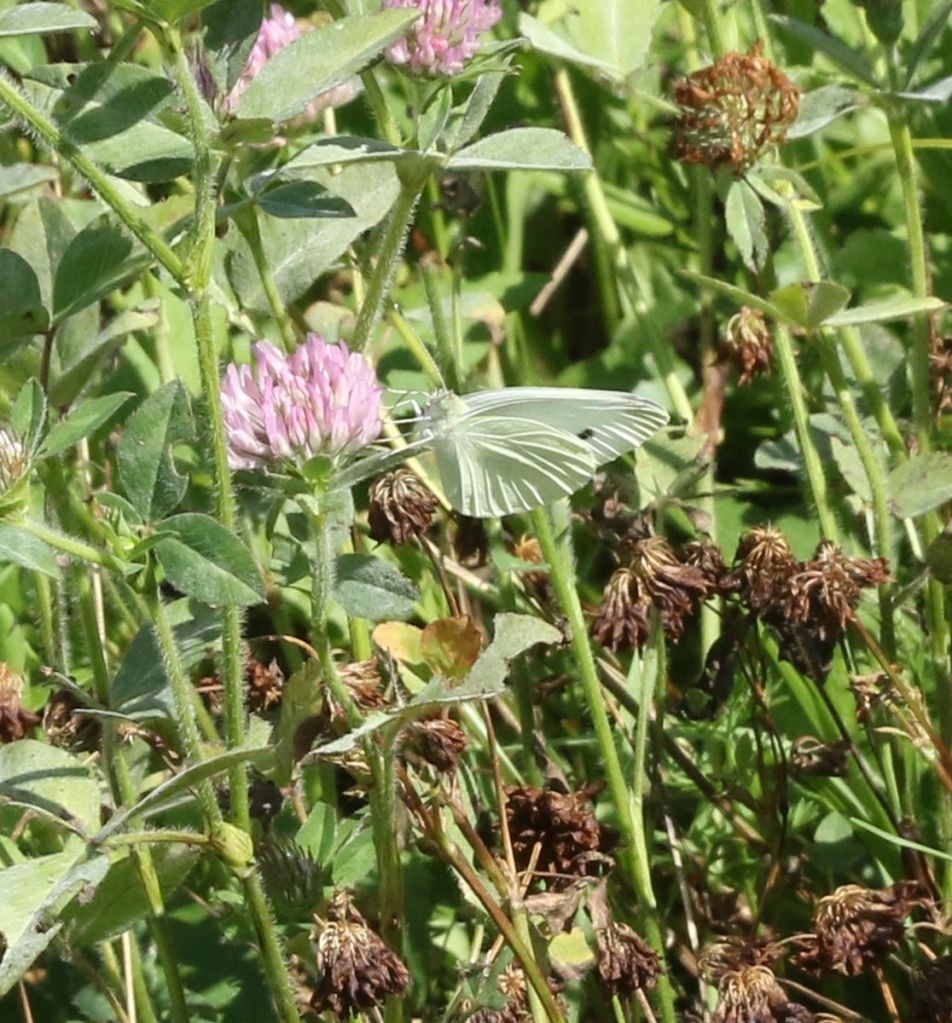

Their medium size and bright white wings is almost distinctive. Just to keep things interesting however…
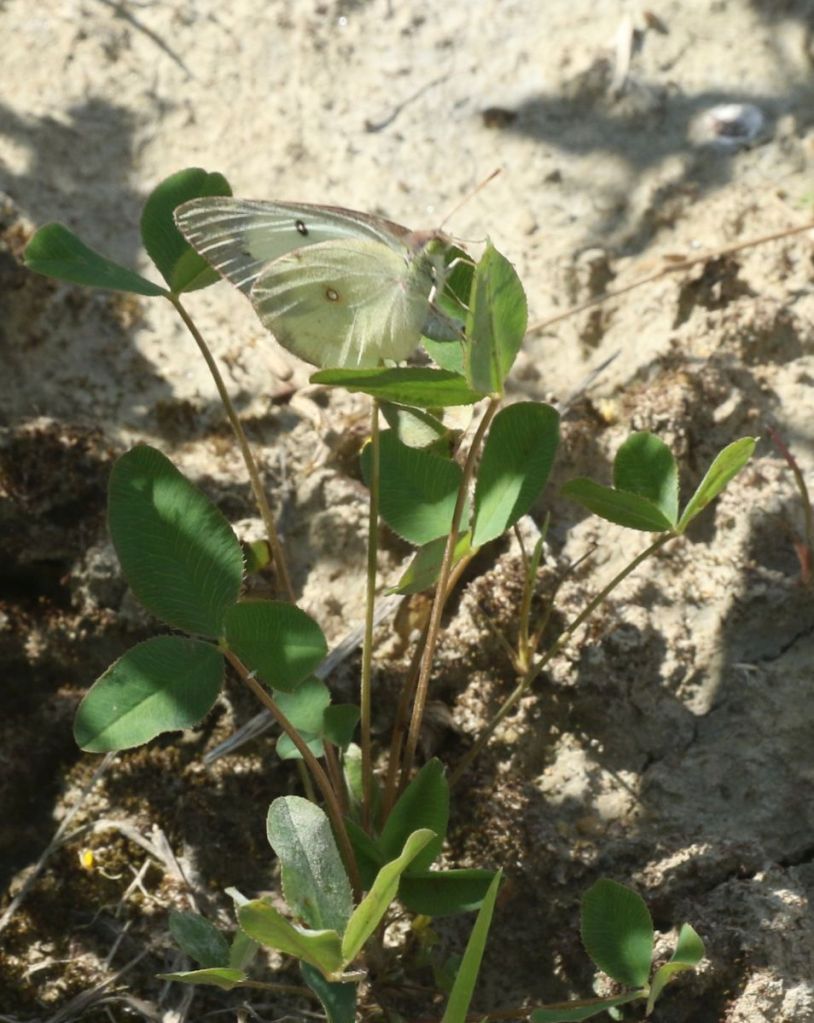

some female sulphur butterflies are white, and so a definitive ID can require a close look. When their wings are closed, sulphurs have a small, brown-outlined eye on their hindwings; Cabbage Whites have no such mark. The tops of the wings are also distinctive but are less commonly seen.
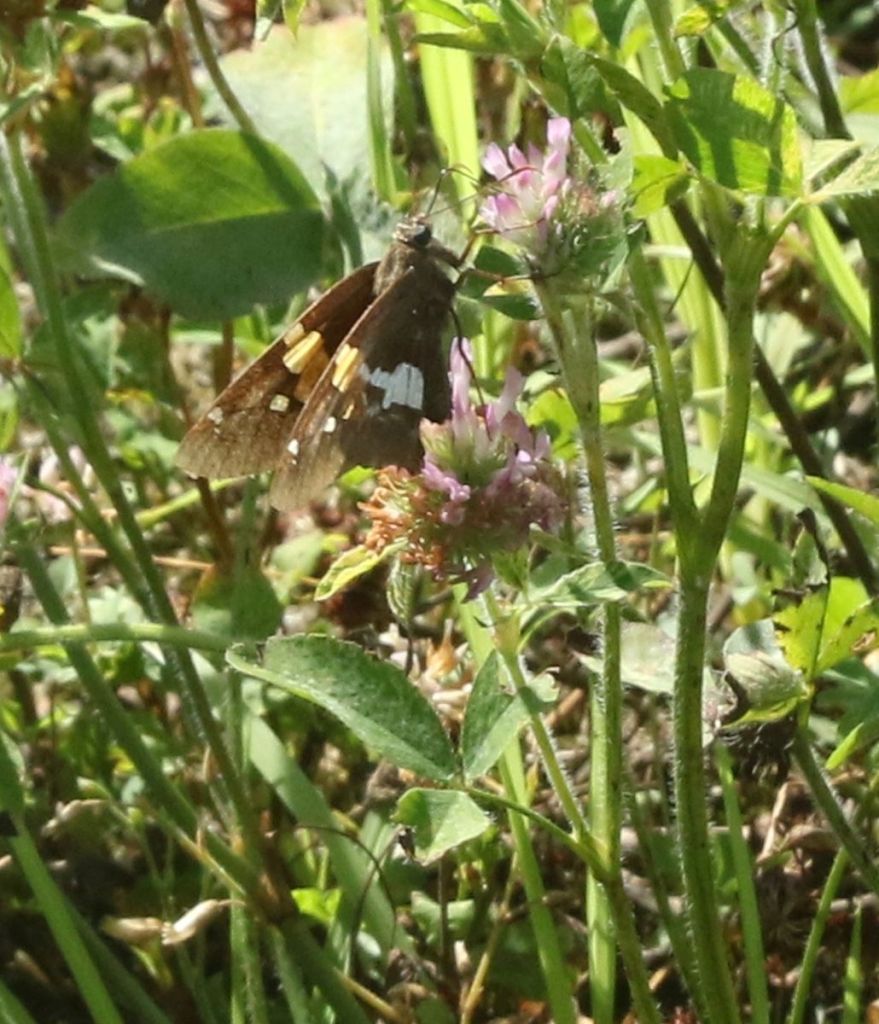

“Skippers” are moth-like butterflies with comparatively large bodies. Their flight is usually hurried, with minimal apparent gliding. This is our largest skipper, the Silver-spotted Skipper. It is a common resident on farms, where its caterpillars feed on various, usually non-commercial legumes.
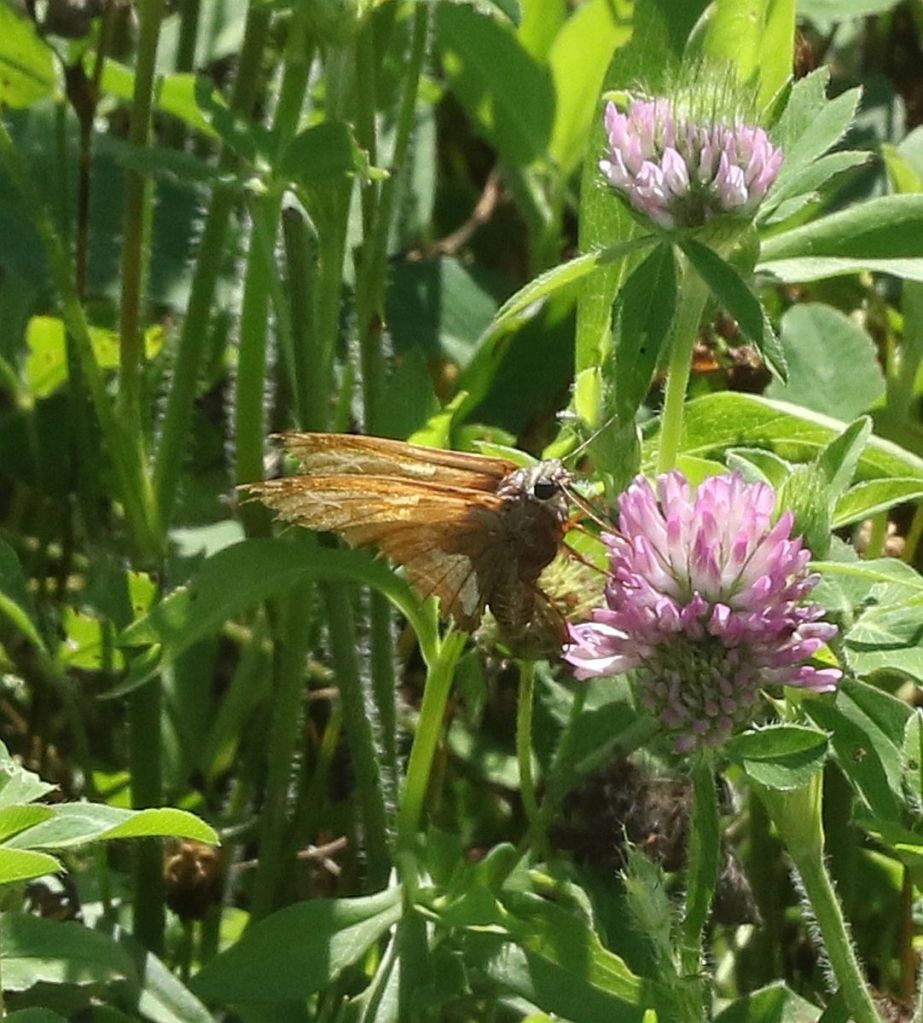

Butterflies do age. Their wings do not grow back and they progressively lose their scales, hence the tattered, almost translucent wings of this Silver-spotted Skipper.
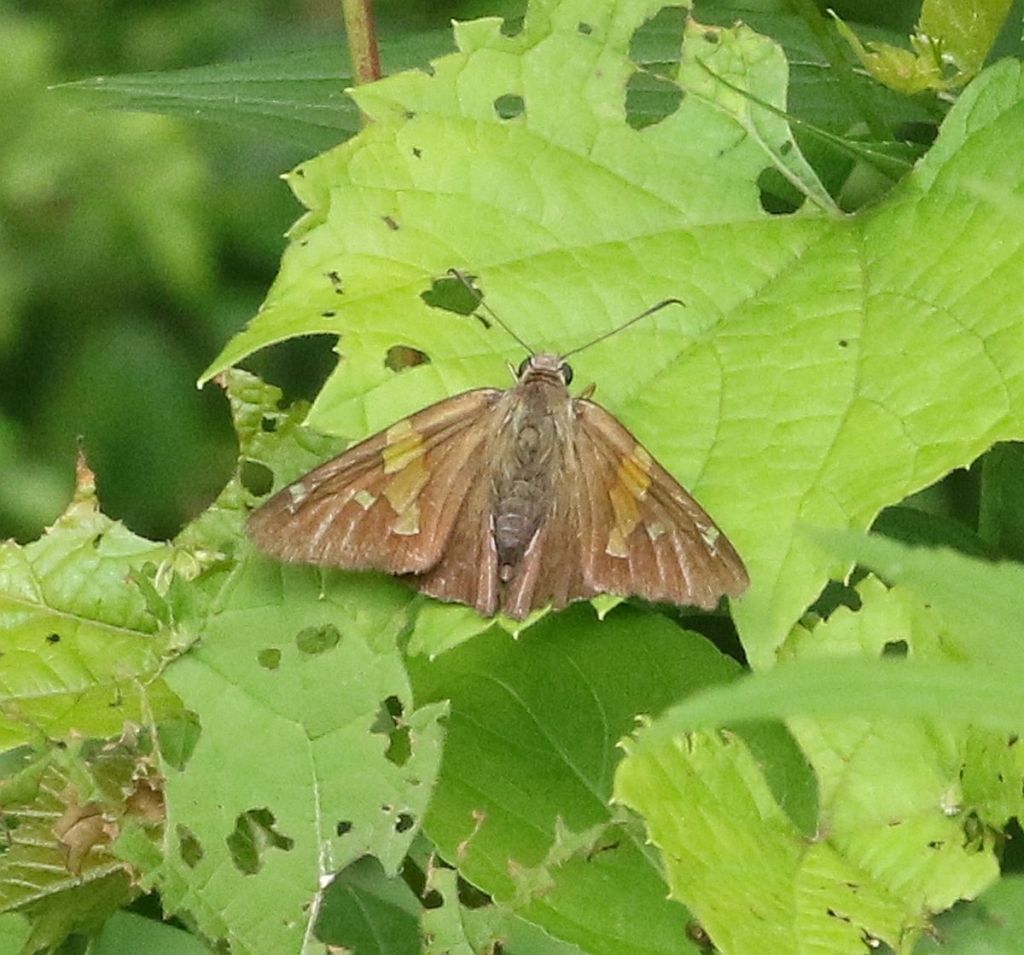

Another Silver-spotted Skipper, this time in the relatively rare open-wing posture.
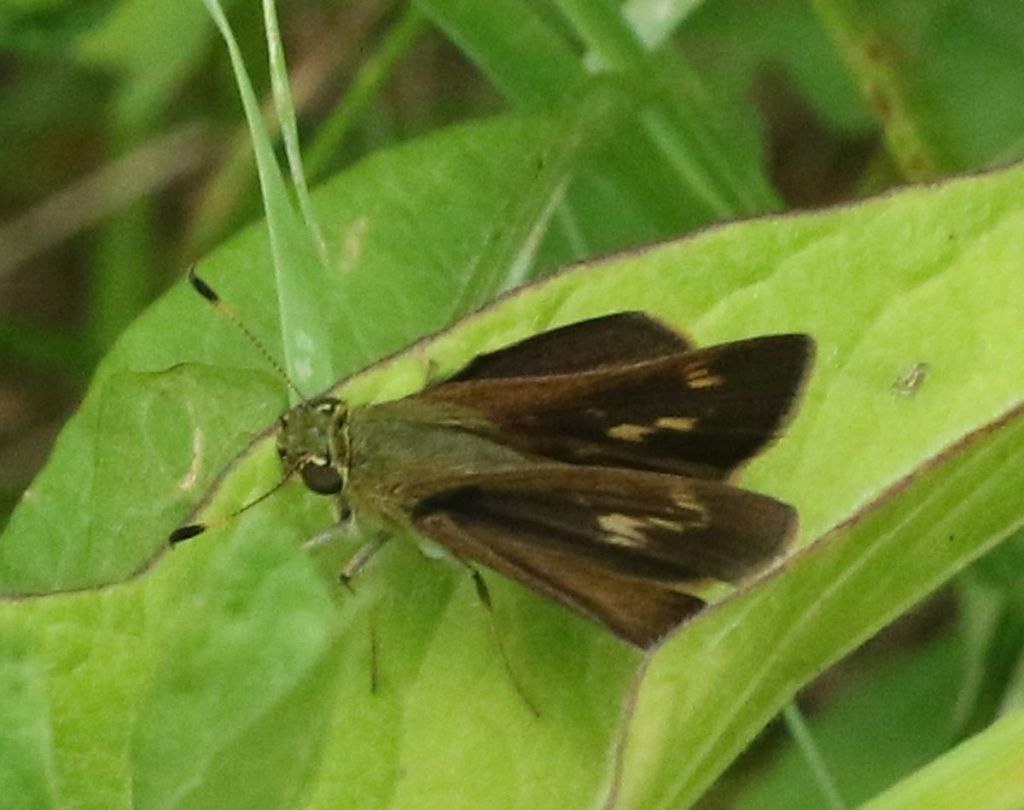

We have a host of tiny skippers that often go relatively unnoticed. They can be tricky to ID, so much so that butterfly aficionados call this and two other darkish skipper species the “Three Witches”. This is a male Little Glassywing, or at least so I have convinced myself!
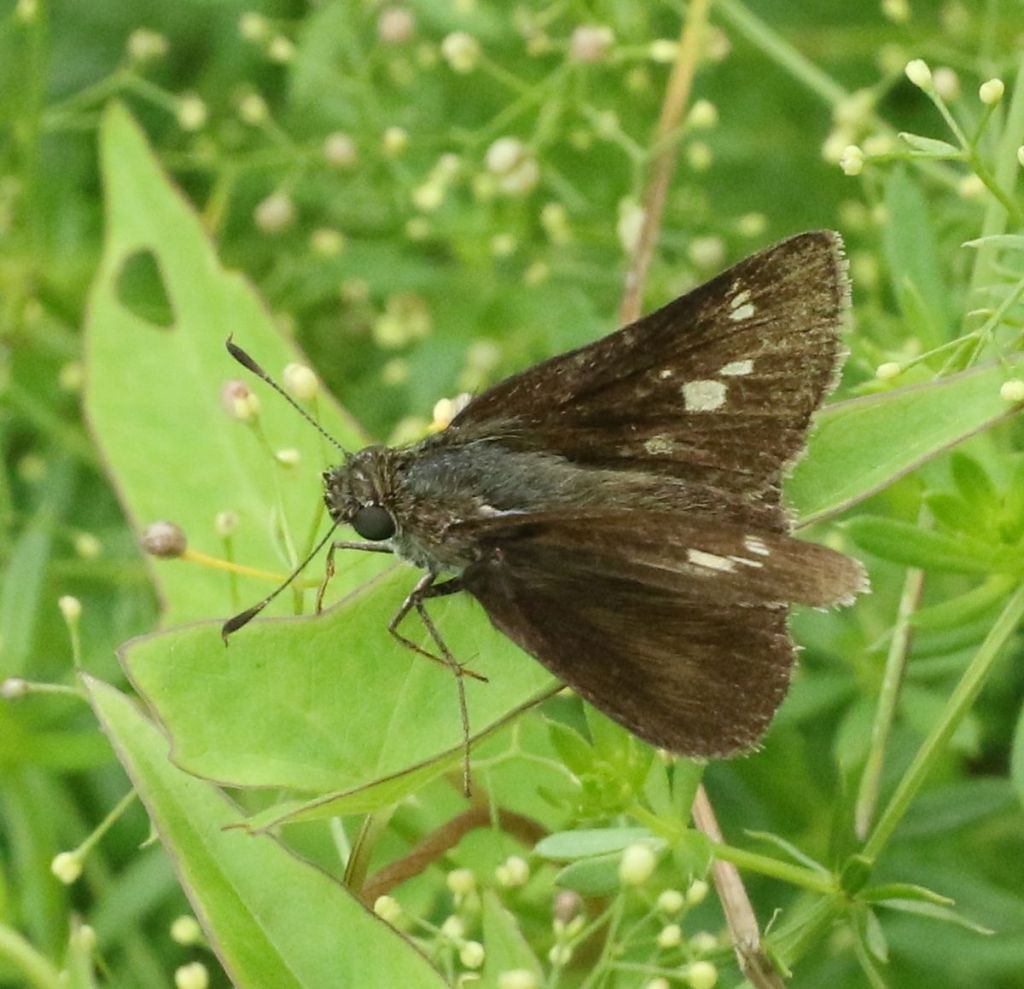

My guess is that this is a female of the same species. These smaller skippers often perch with their wings in a ‘jet-fighter’ position – the hindwing flat and the forewing at an angle.
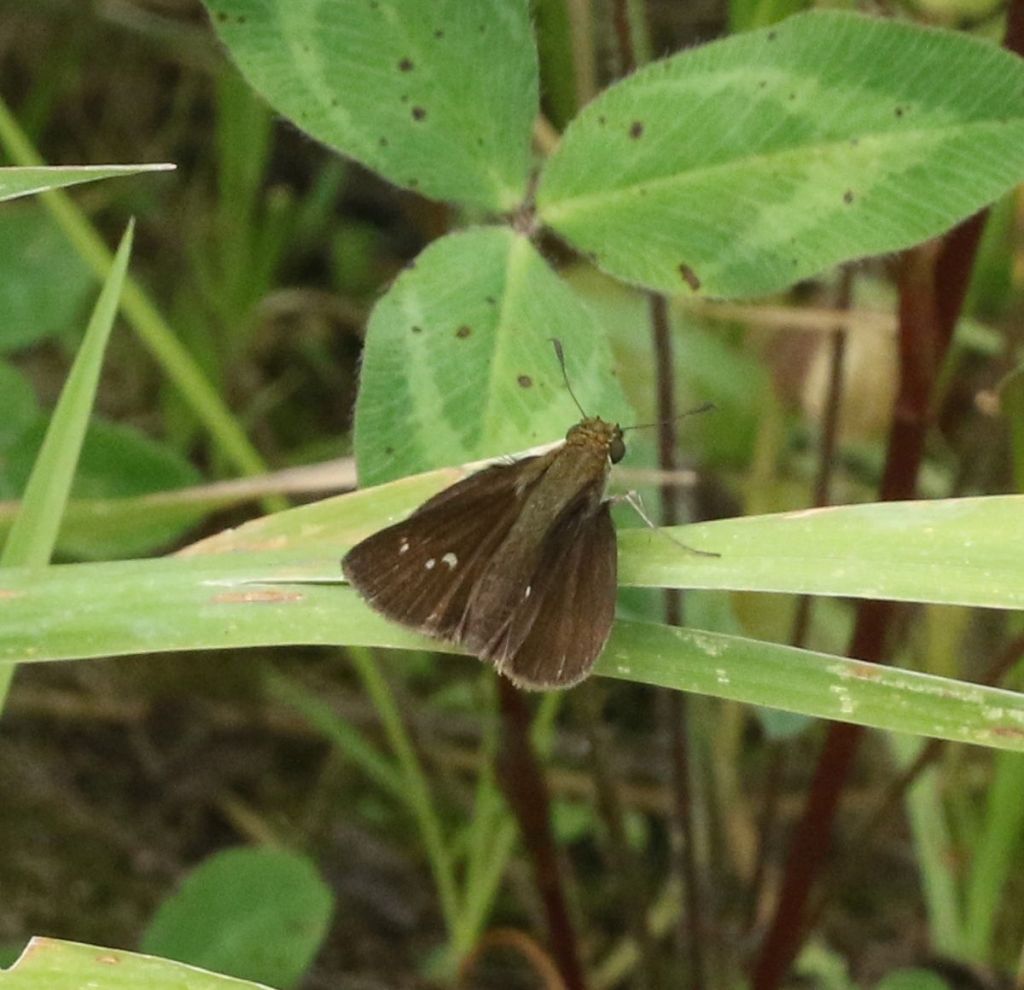

I believe this slightly drabber-colored species is a Dun Skipper, another one of the witches. Unlike the other two witches, the Dun is a sedge feeder; correspondingly, it tends to be most common around wetter areas.
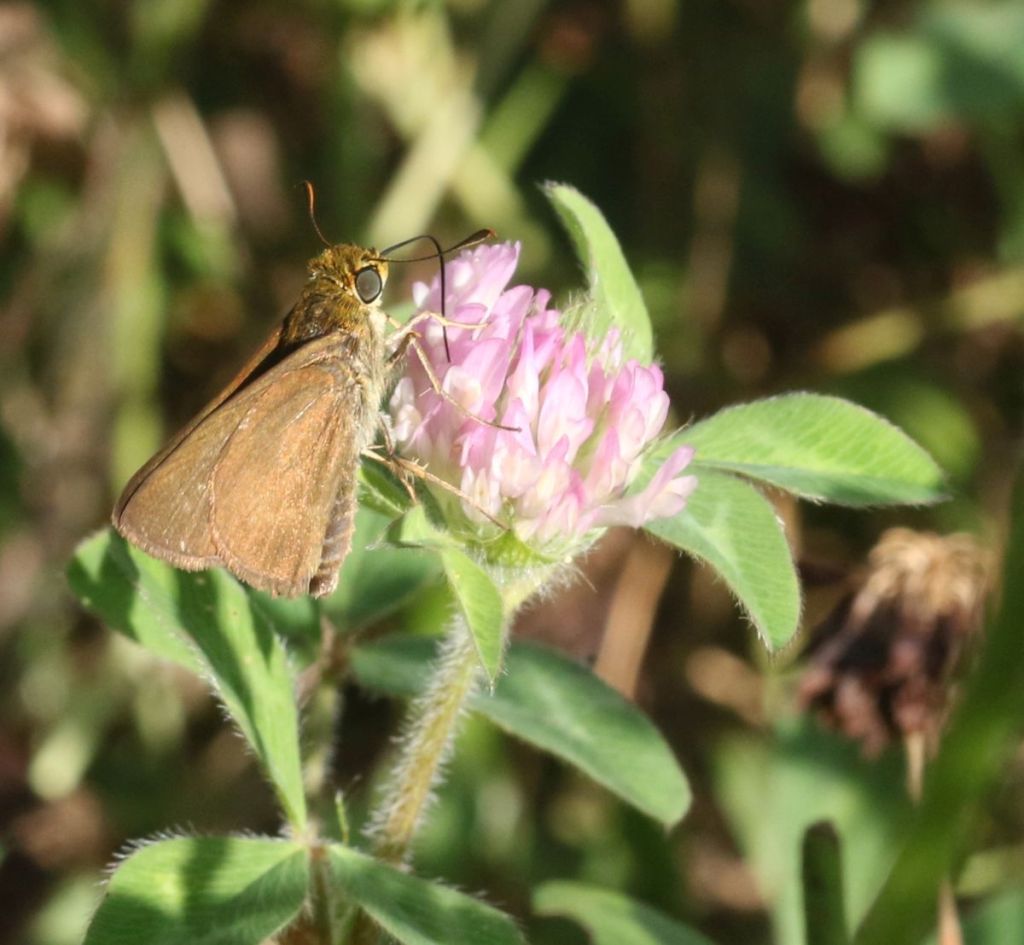

The bronzy head of this fresh individual is a subtle but useful characteristic for recognizing the Dun Skipper.
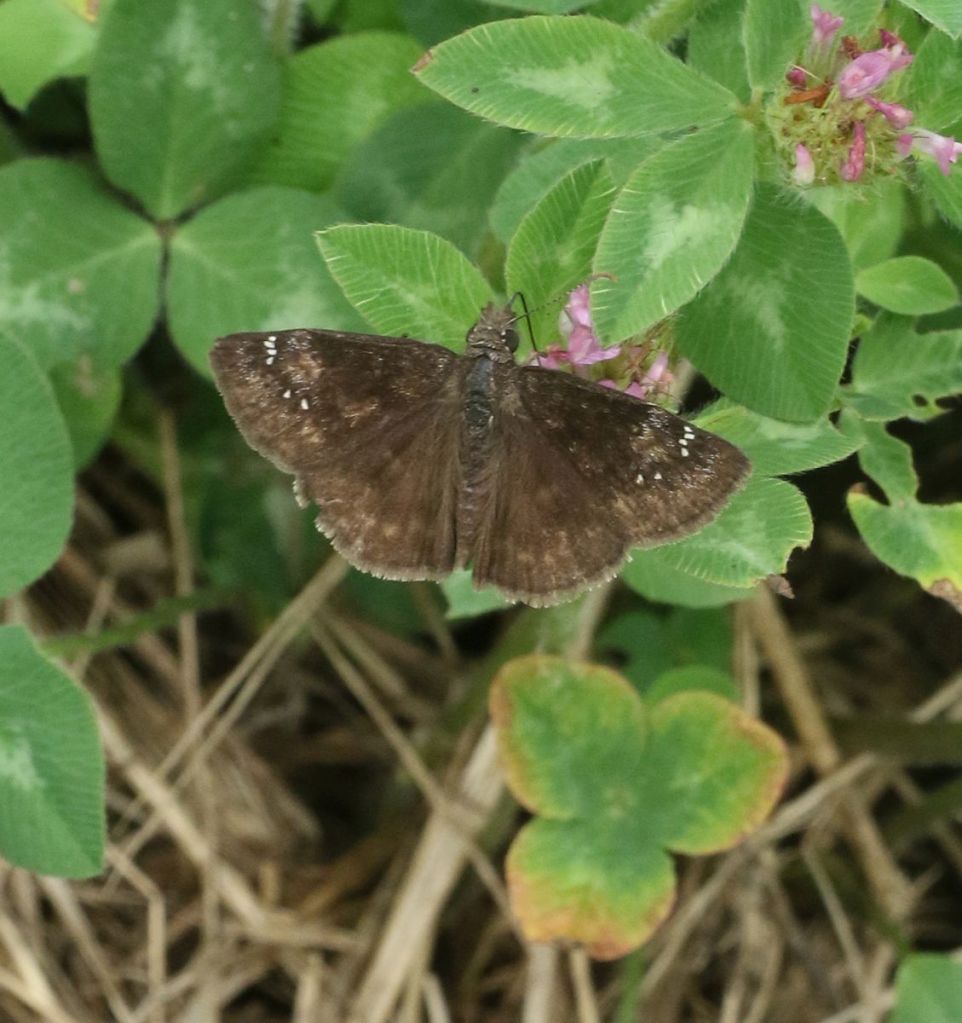

Some skipper do, however, perch with their wings flat. In fact, one rarely sees these particular species with their wings closed. This is a Wild Indigo Duskywing, a native butterfly whose caterpillars feed on Wild Indigo. This would currently seem to be a losing strategy in our region – how many times have you seen Wild Indigo? However, species aren’t stupid evolutionarily, and the Wild Indigo Duskwing could now be more aptly named the Vetch Duskywing, having accepted introduced vetches into its diet.
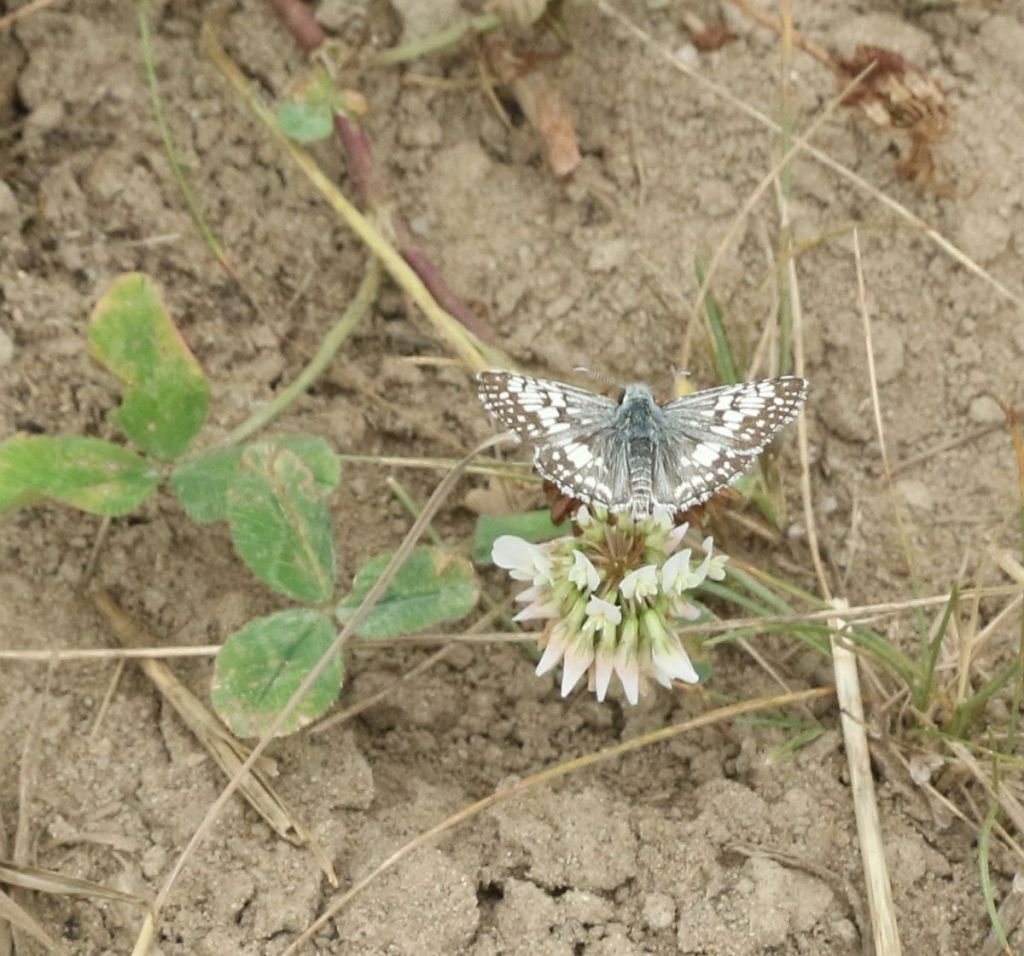

This was the first time I have seen a Common Checkered Skipper for at least a couple of years. We are on the northern edge of this southerly species’ range, and they have not been common locally. It may not overwinter with us and might need to recolonize each summer from farther south. Its caterpillars feed on Velvet Leaf, a farm weed that Sue assured us she has plenty of.

This little beauty is a Pearl Crescent – a small, sometimes common butterfly whose caterpillars feed on asters. They were most common in the flowers between the pond and the forest, but were found throughout the farm.

A mated pair of Pearl Crescents, the larger, more darkly marked female has her wings open.
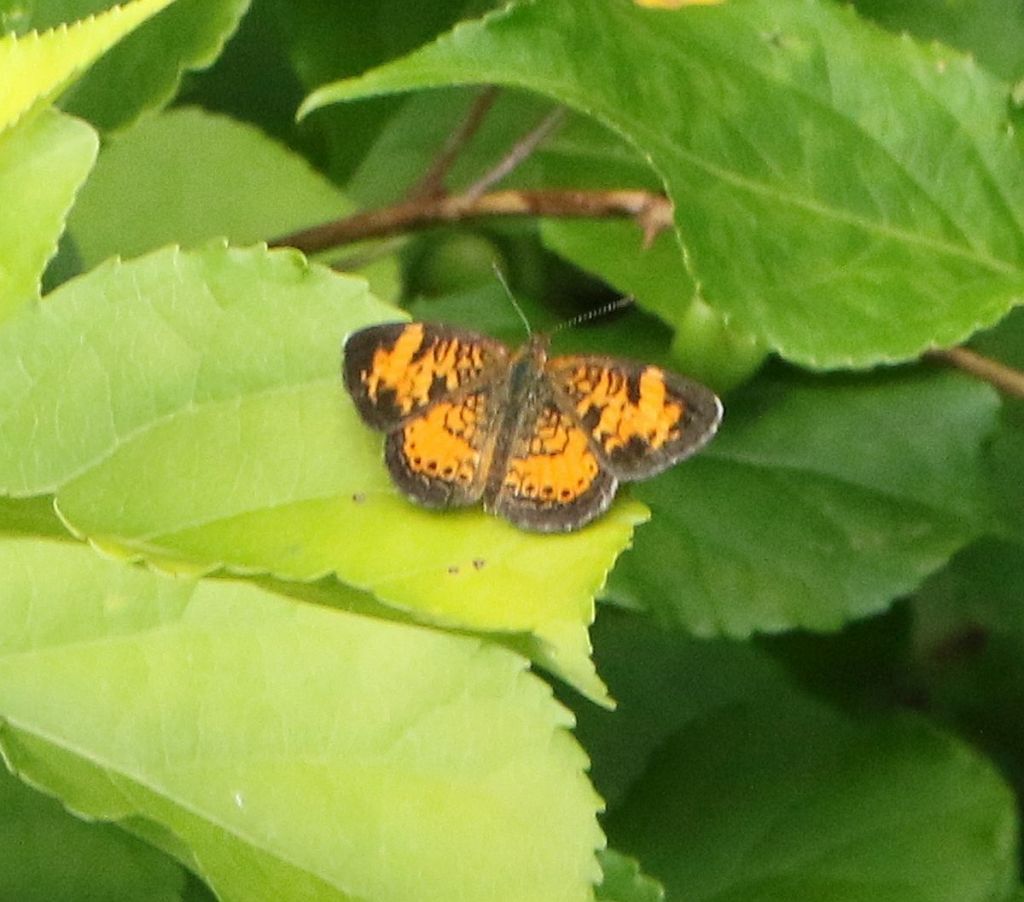

Crescent taxonomy harbors some confusion. There are probably at least two Crescent species in the County, the widespread Pearl Crescent and the less common Northern Crescent. The distinguishing characteristic is said to be the lack of black dividing lines in the central, orange field of the Northern’s hindwing. So perhaps this is a Northern Crescent, or maybe it’s just a particularly ‘blond’ Pearl Crescent.
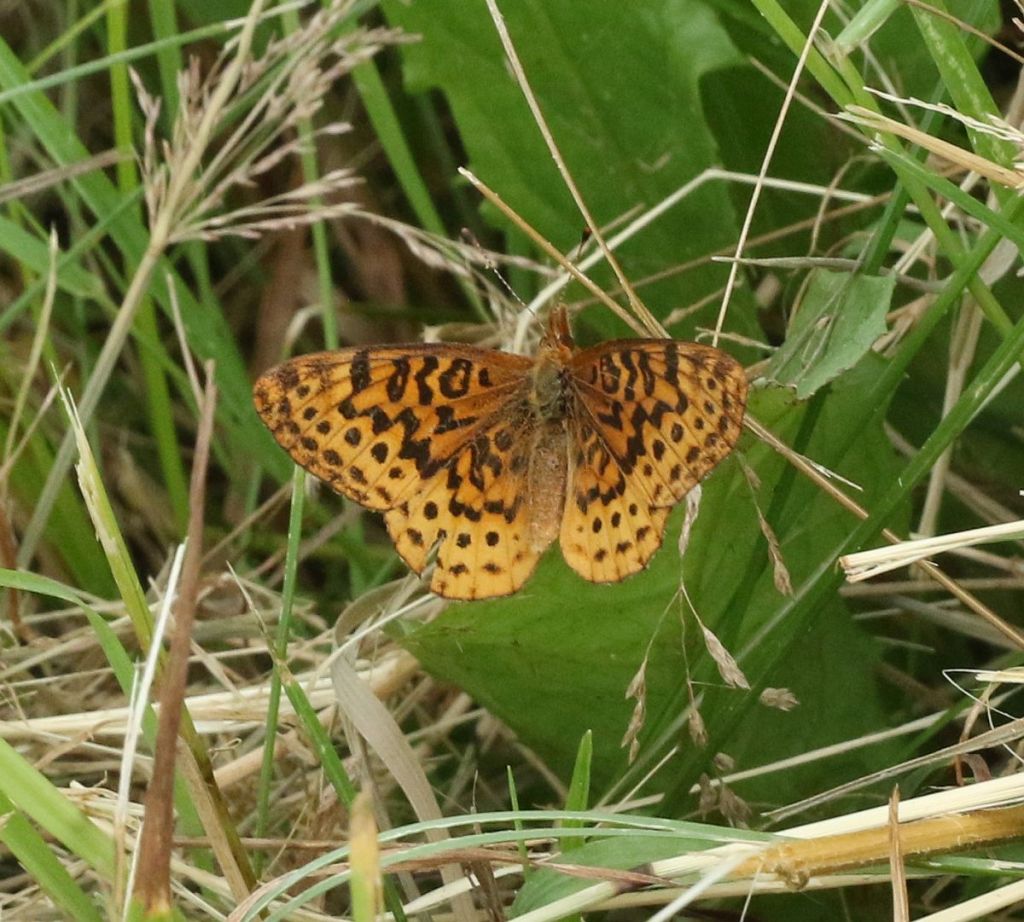

Only slightly bigger than a large, female Pearl Crescent, the Meadow Fritillary seems to be declining regionally for reasons unknown. In the 19th century, for example, its range extended throughout Massachusetts, but now it is mainly found in the western part of the State. It has similarly retracted from the surroundings of NYC. One hopes it will not go the way of the Regal Fritillary – a once relatively widely distributed species, now nearly extinct on the East Coast.

The Meadow Frit’s underwing is well camouflaged.
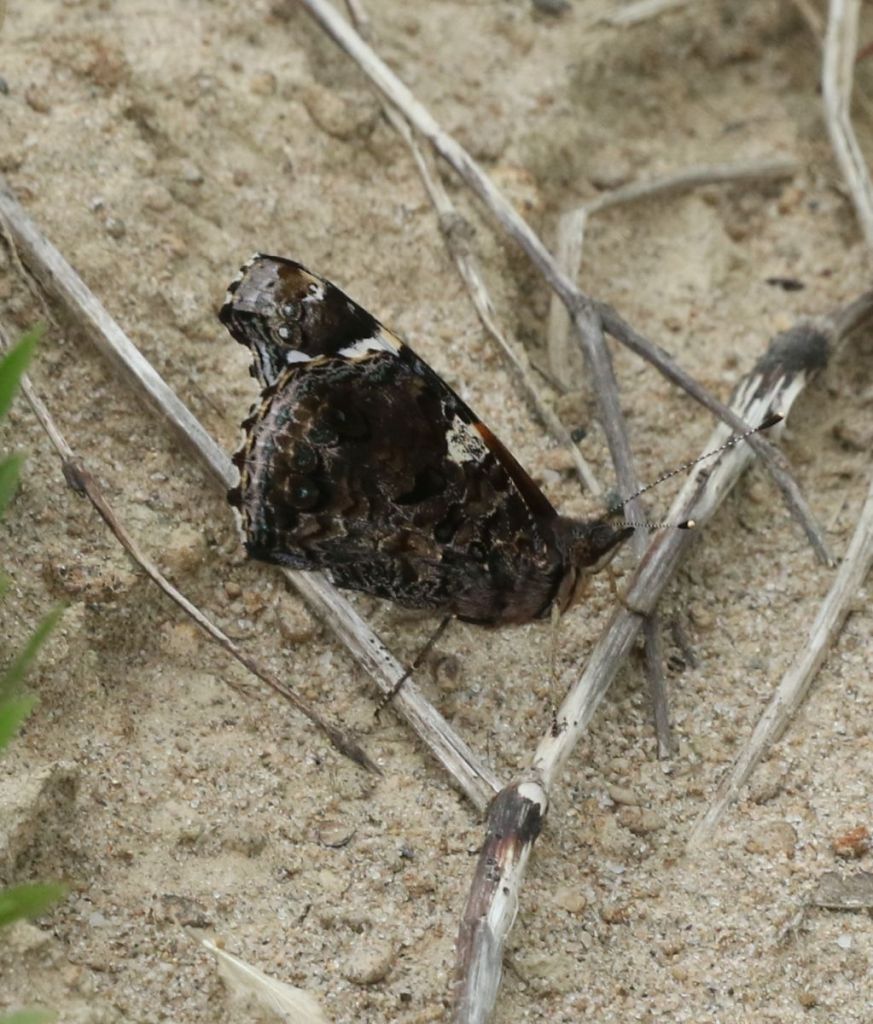

The underwing of this butterfly is also subtle, but, wait a bit and…
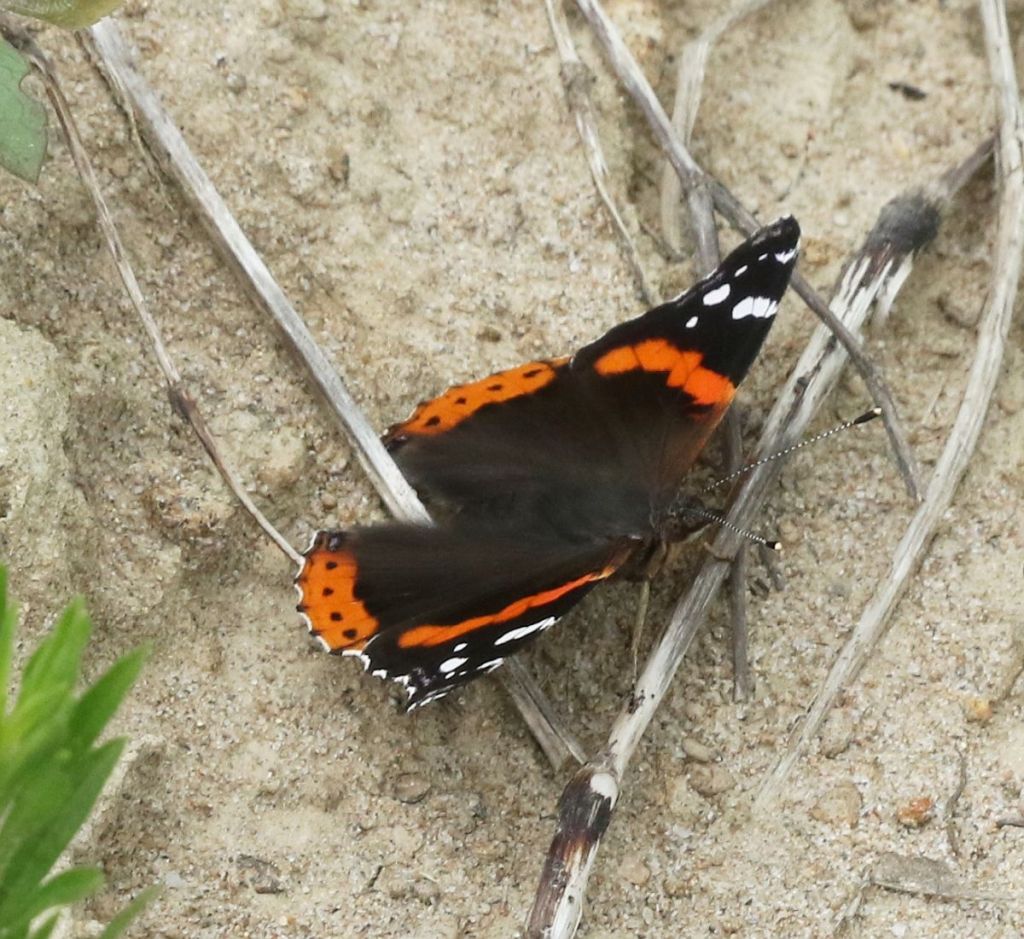

the Red Admiral may flash its more dramatic wing tops. Like the Monarch (and a few other of our species), the Red Admiral is migratory.
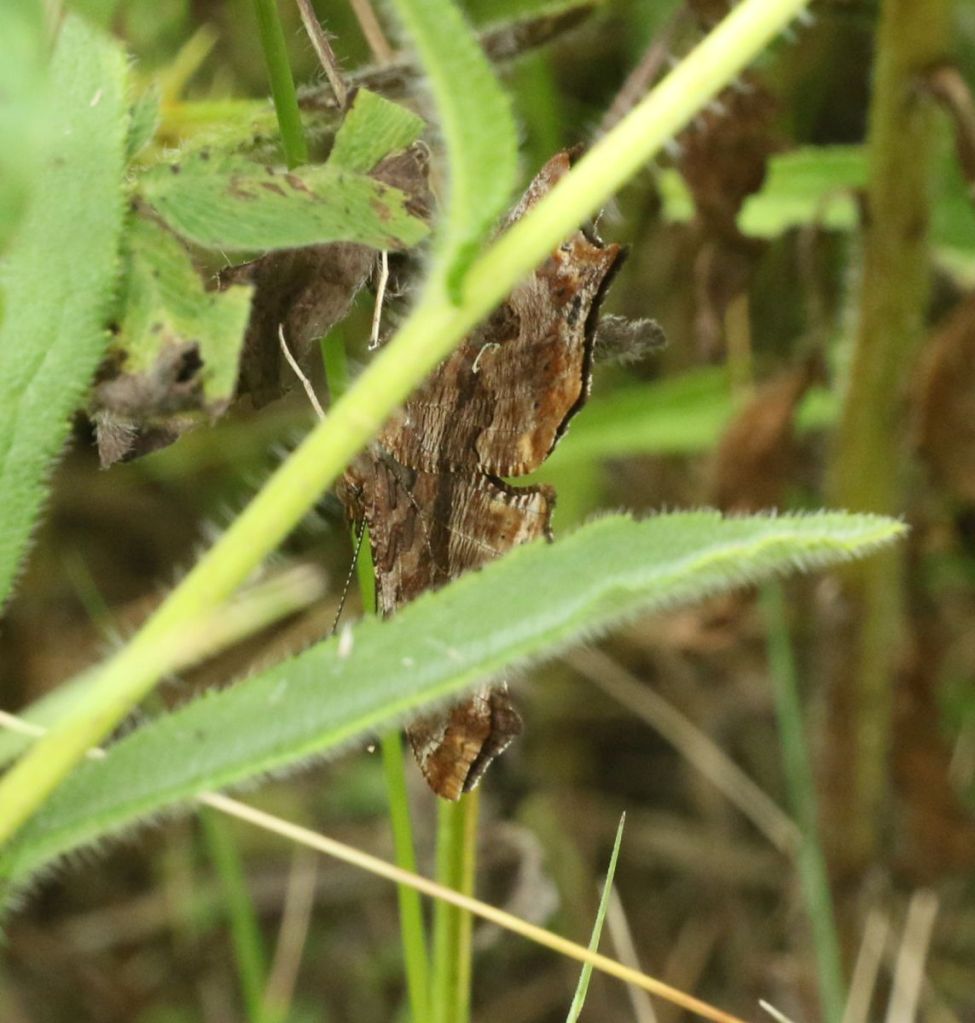

Do you see the butterfly hiding in this picture?
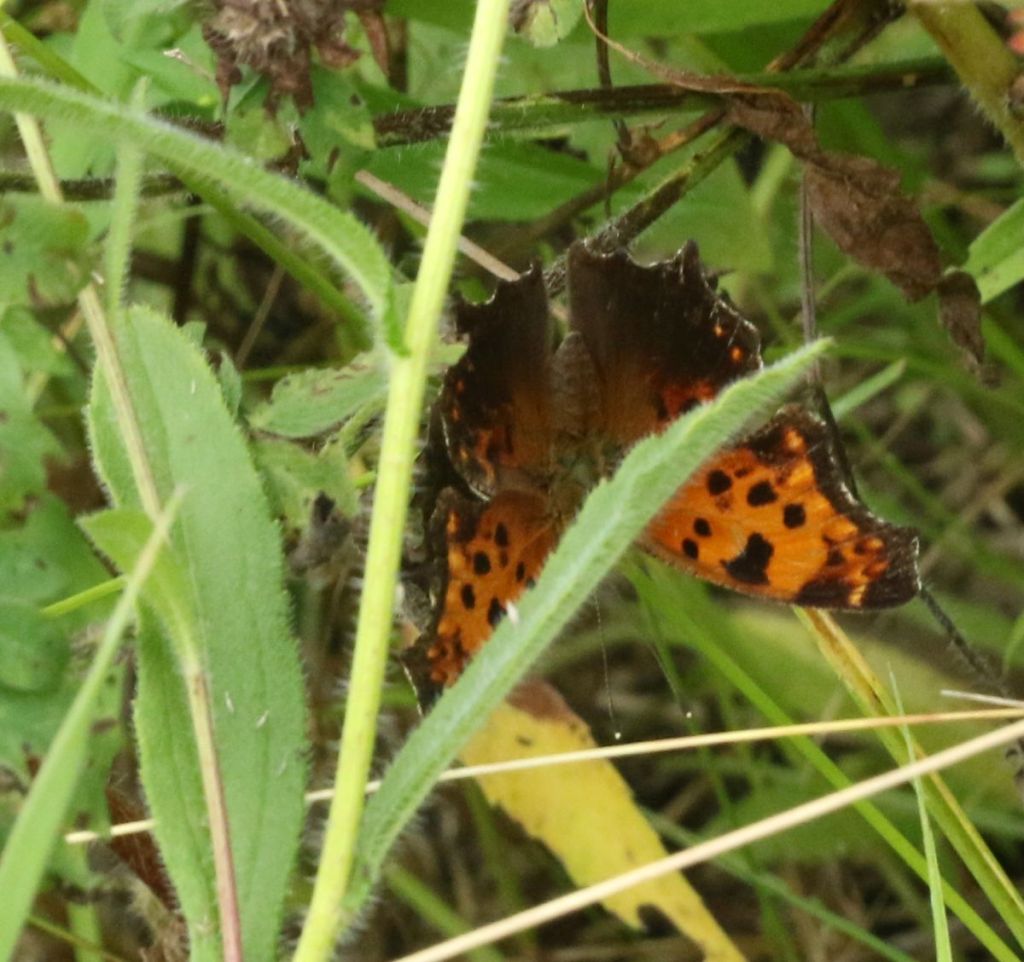

What about now? This is an Eastern Comma. It is thought that such contrasting coloration of the two sides of the wings might play a role in a startle strategy – come too close and a potential predator gets a surprising flash of orange as its intended prey flies away. Alternatively, perhaps the coloration plays a role in inter-species communication but is best kept under wraps much of the time.
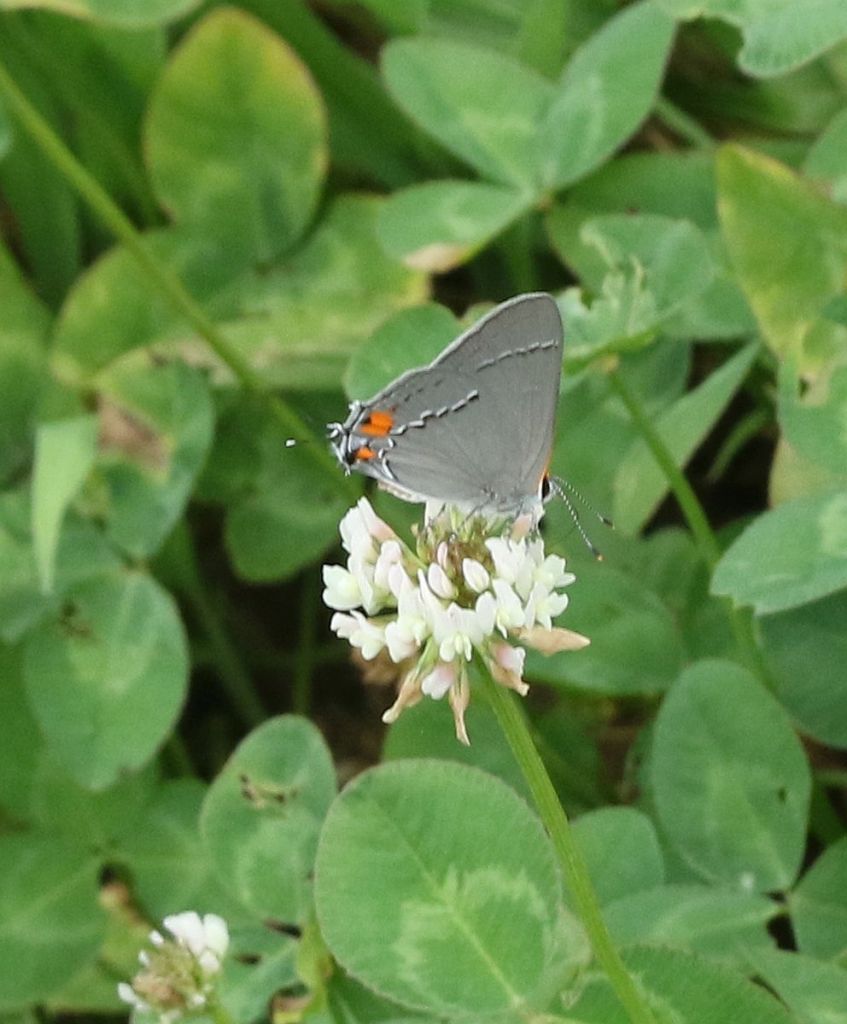

As suggested by the fact we have already seen this hairstreak in our Little Seed Gardens posting, the Grey Hairstreak is probably are most common hairstreak.
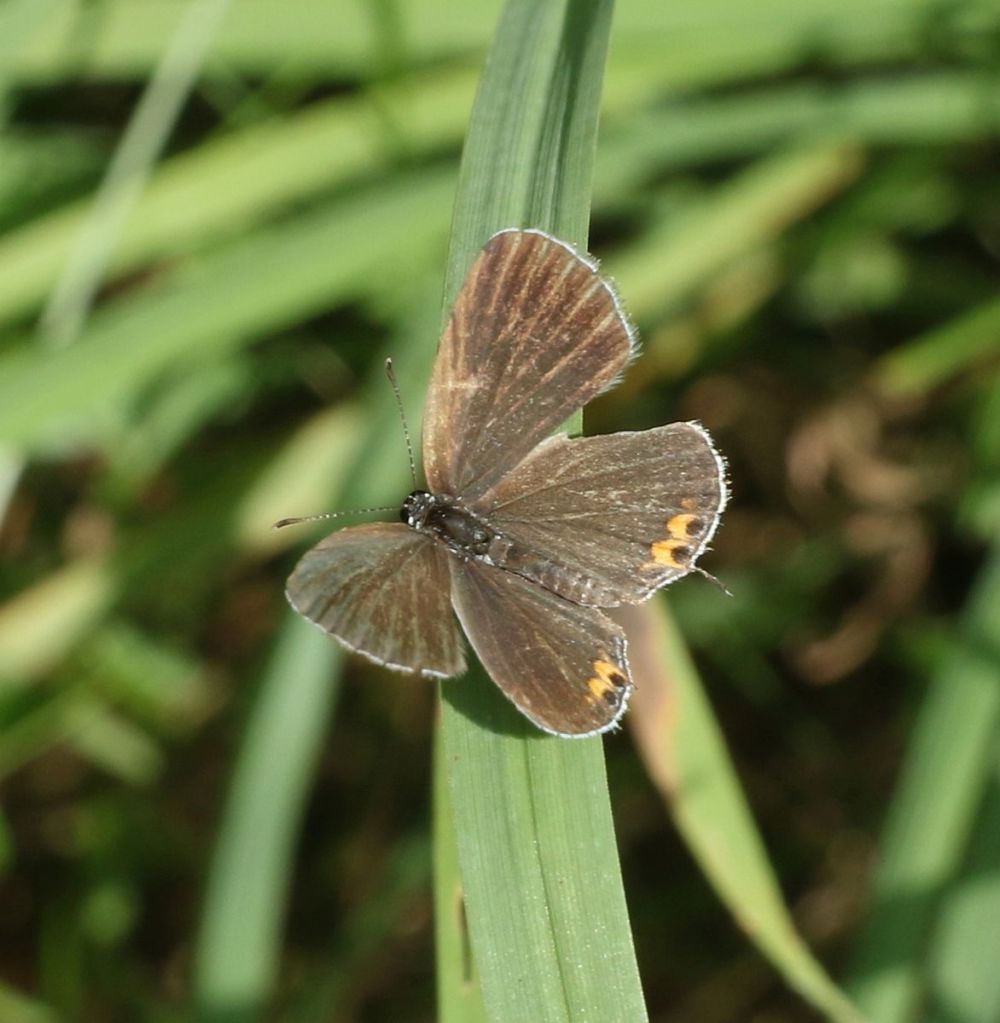

A sooty Eastern Tailed-blue female.
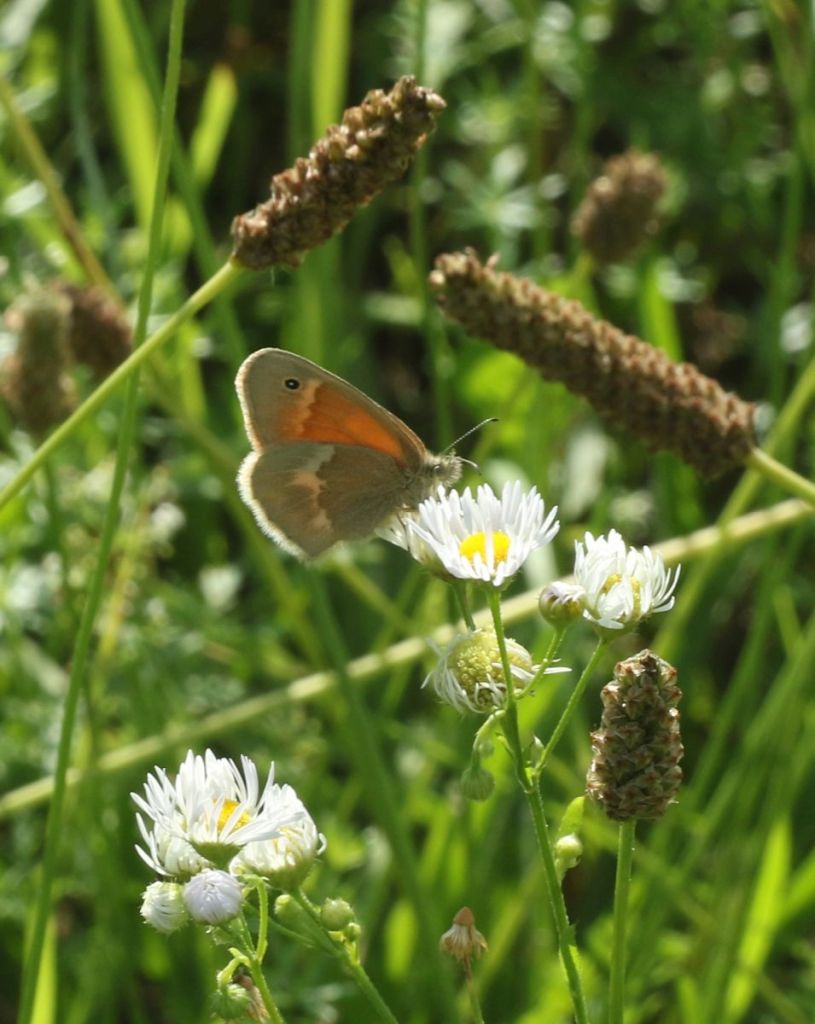

Common Ringlets flash their brick orange while flying. Somewhat counterintuitively, this is a northern species which has come south over the past 30 years or so.
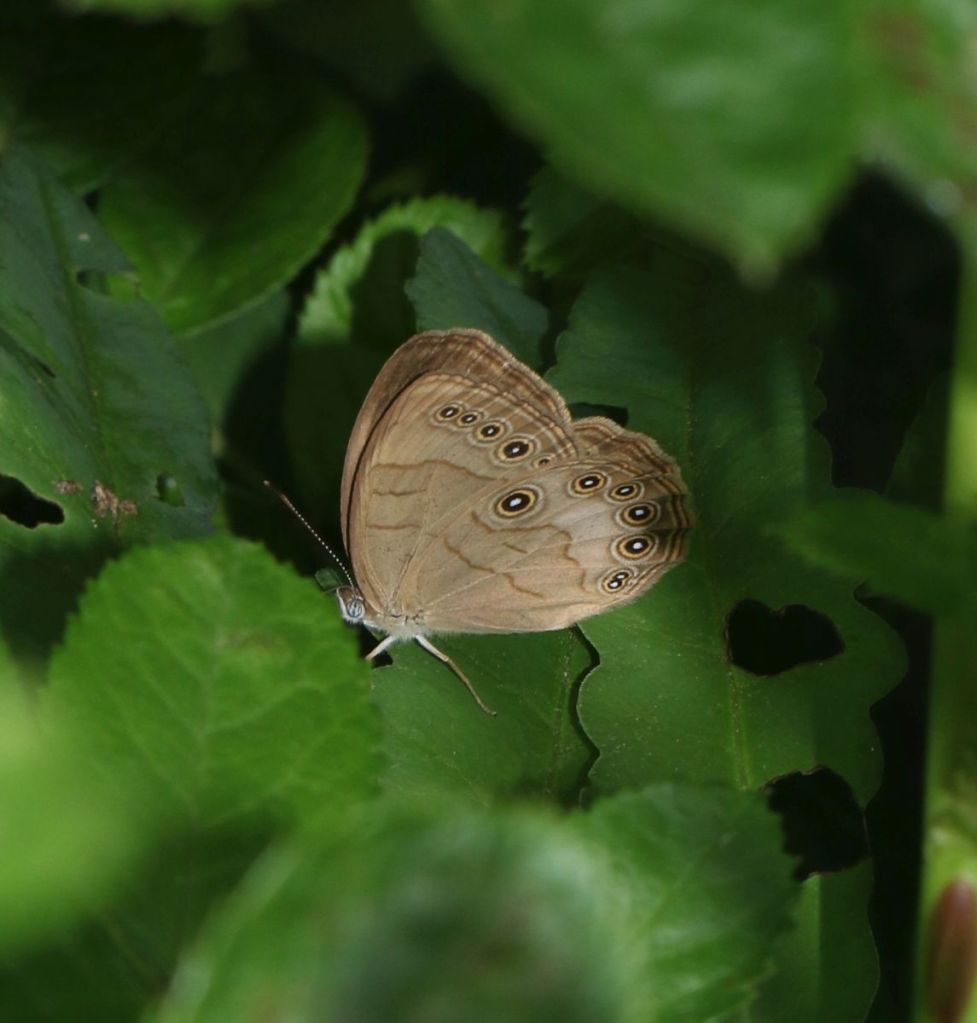

This reclusive butterfly was found hugging the edge of the swamp forest. The Appalachian Brown is largely confined to wetlands, where its caterpillars’ food plants – sedges – are found. Unlike some other wetland butterflies, one rarely sees it on field flowers, perhaps because tree sap and animal dung are its more favored adult foods.
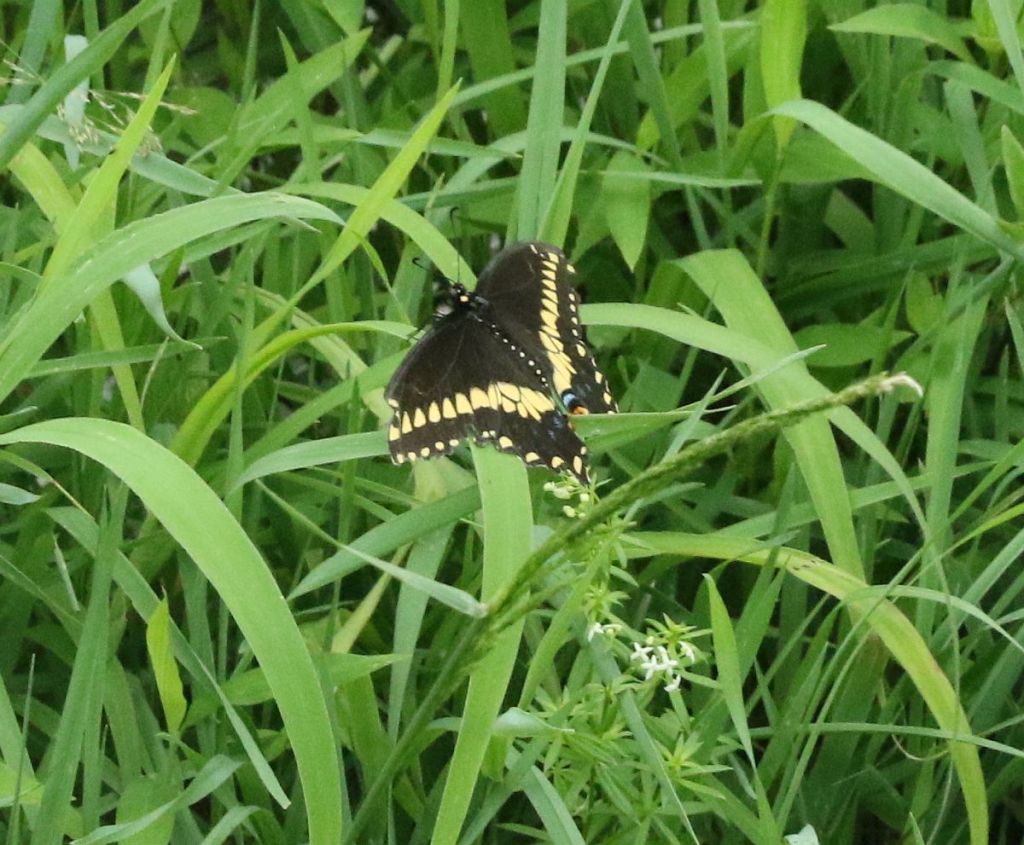

A male Black Swallowtail decked with ample ‘scrambled eggs’.

The female has less yellow. This is a native butterfly, but is sometimes considered an agricultural pest on carrots, dill, parsley and other cultivated relatives. Caterpillars also feed on Queen Anne’s Lace.
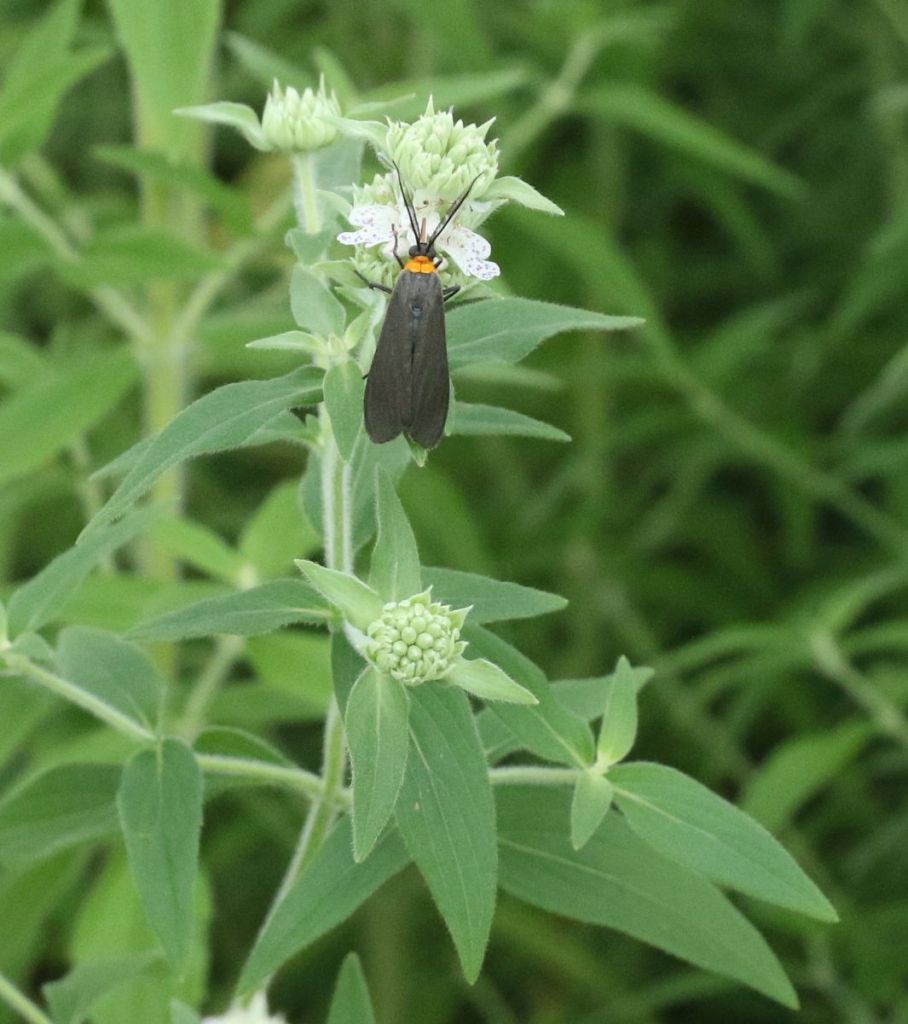

Butterflies aren’t the only ‘Lepidoptera’ out during the day – several of our moths are also day fliers. These Yellow-collared Scape Moths seem especially common this year. Their caterpillars are reportedly grass and sedge feeders, but the adults seem to love nectaring on a range of flowers.
None of the butterflies we saw at this farm were particularly rare, but their abundance and diversity (18 species) were encouraging. This was probably due in part to the diversity of habitats on the farm, from wet meadow to swamp forest to pasture to pond edge, combined with the ecological farming practices used and the ample space for wild-growing flowers.
The dragonflies and damselflies around the new pond were fairly abundant, especially for a pond that is only a couple of year old. One of the key factors that encourages the diversity of these insects is a lack of fish, and we would discourage their introduction. If it does not completely dry out, there might be additional species of dragonflies in the swamp forest, but we did not venture in during this visit.
Stay tuned for Claudia’s plant contribution.
