by Claudia
This blog shares some of the botanical observations from Churchtown Dairy on 19 July 2024. Will had visited the farm separately and written about the “Birds of the prairie” at this farm in his blog posted on 13 October 2024.
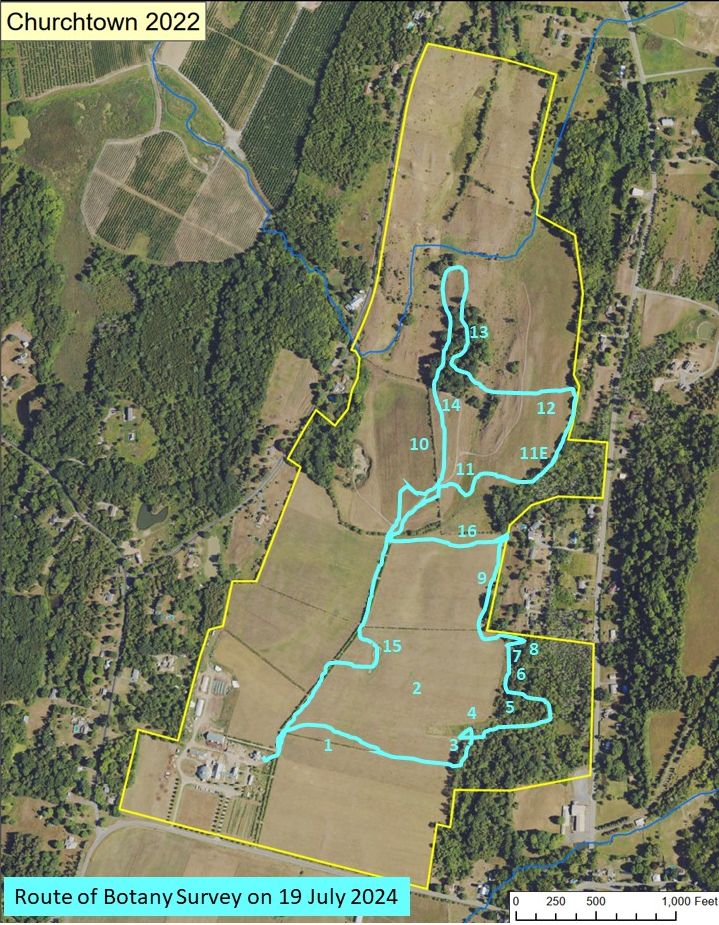
The following map shows the approximate route walked for the botany survey. The numbers (referenced throughout this blog) indicate places where botanical observations were made or pictures were taken.
Let us begin by sharing some habitat images from the farm:
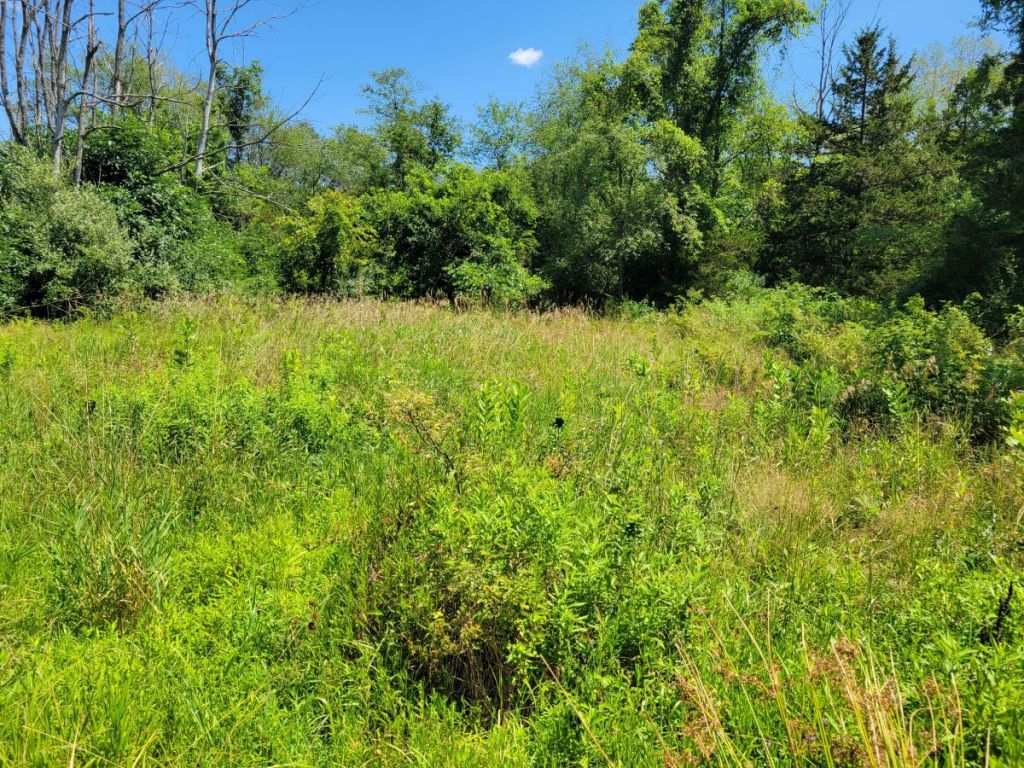
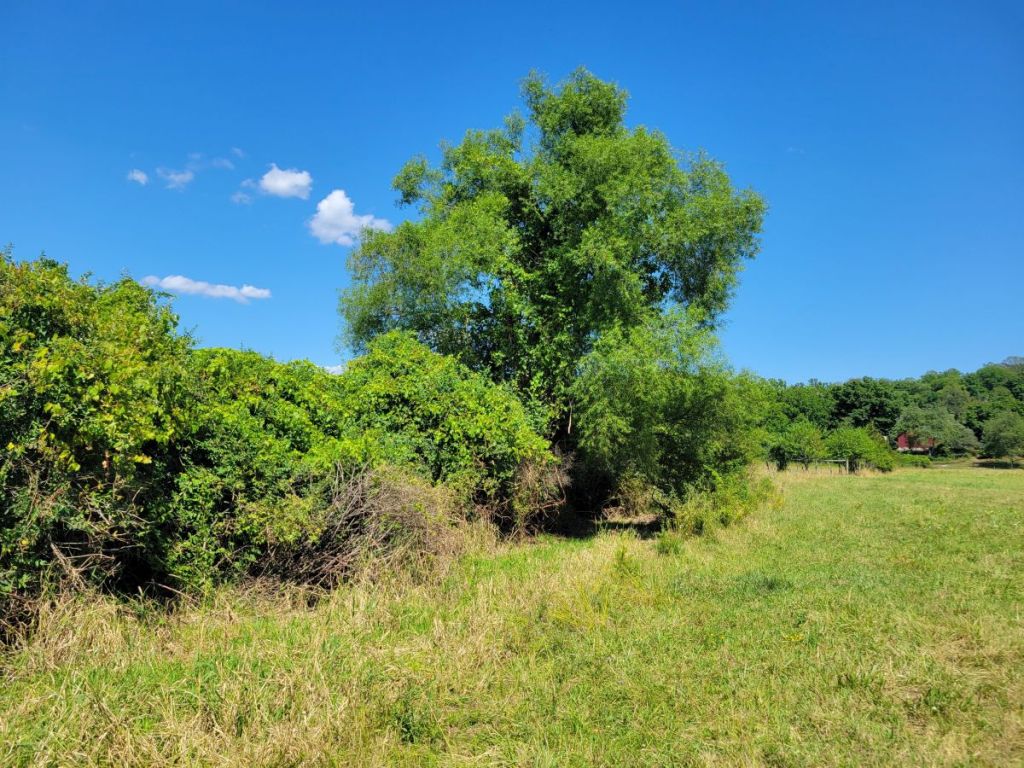
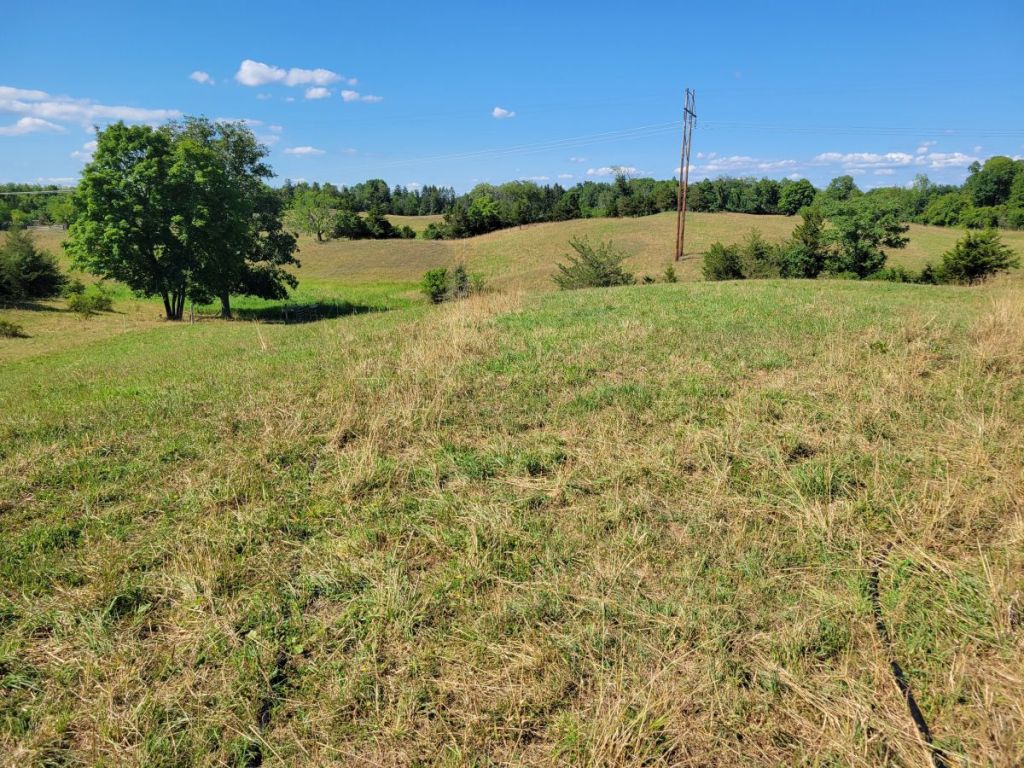






After this brief visual introduction to the farmland at Churchtown Dairy, we’ll go into more botanical detail.
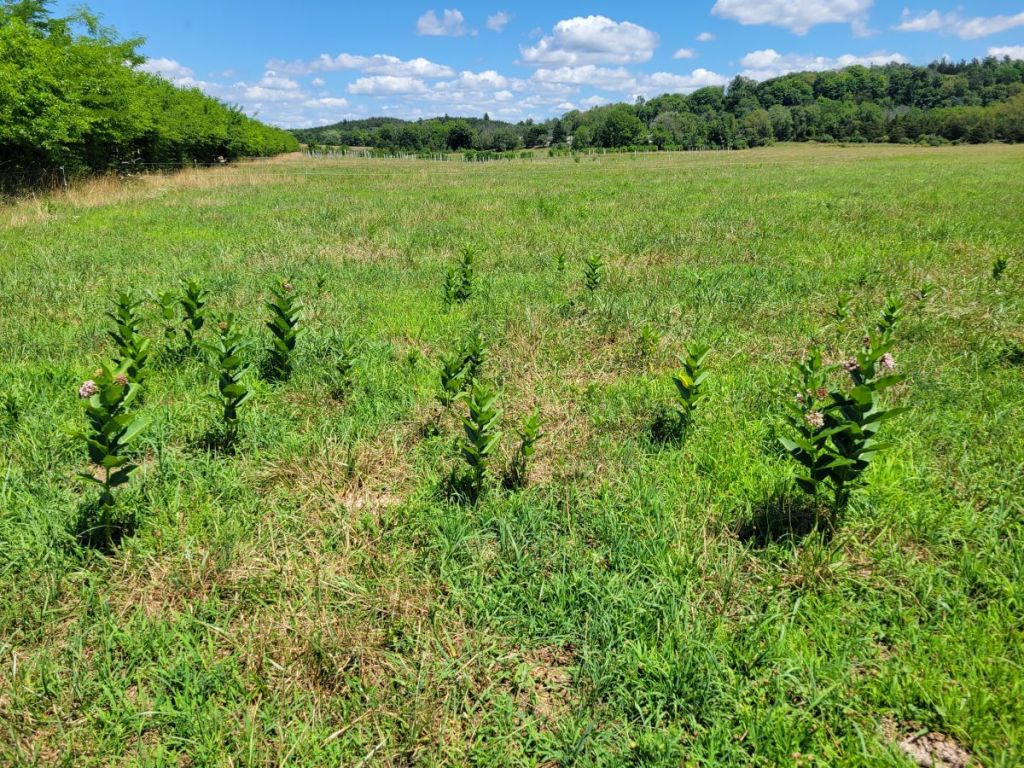
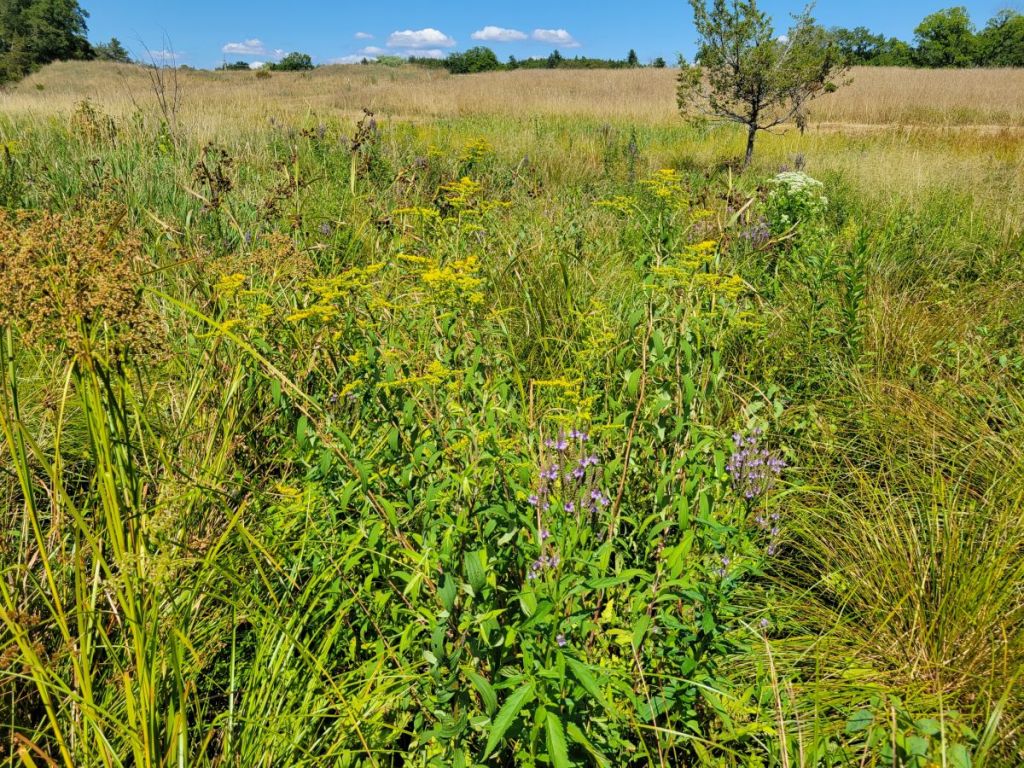
Most of the pastures were closely-grazed at this point. As typical for pastures and hayfields in our region, most of the plants in the pastures themselves were European species of grasses, legumes, and other common plants of perennial agricultural meadows. One exception stuck out immediately: many of the pastures had patches of Common Milkweed, a wildflower native to North America and one of the host species for Monarch caterpillars, as well as a number of other native milkweed-specialists. It was nice to see that the milkweed plants across the farm were at different stages of development, some going to seed, some in mid-bloom, and some just beginning to put out new leaves after having been grazed or clipped. Maintaining such diversity of developmental stages throughout the growing season is beneficial for the insect community, because it ensures the availability of a variety of resources (ranging from tender leaves for young caterpillars to nectar for adult butterflies and many other insects) for an extended time period (compared to the scenario were all plants of a species mature and go to seed at the same time).

The hedgerows and forest edges bordering the pastures were composed of a variety of native and non-native woody plants. The hedgerows bordering the central laneway and separating some pastures had been planted relatively recently (10-20 years ago) with a small selection of species, including Osage Orange and Honey-locust (both considered native to areas south of here), and hawthorn and hazel (species and native status uncertain). However, the longer-established hedges and field edges supported wild-growing, native Staghorn Sumac…

… Red Cedar …

… and even an occasional stately oak (pictured here is a Red Oak, whose leaves were partly eaten by Spongy Moth caterpillars)…

… and a willow, probably the native Black Willow (Salix nigra).
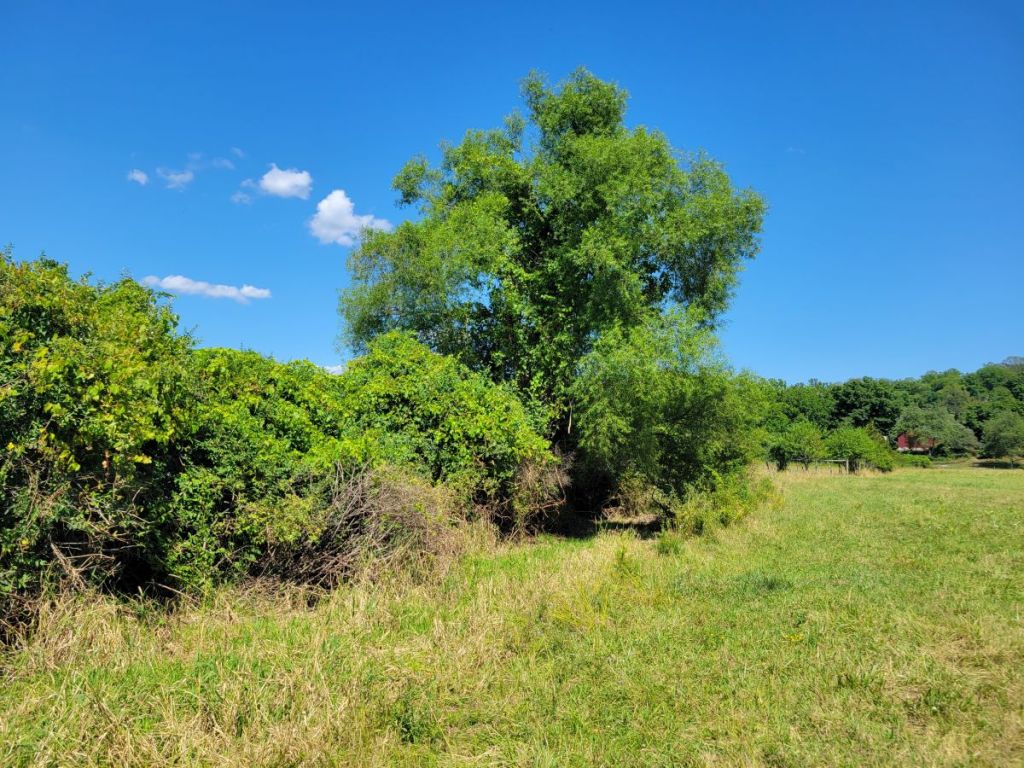

Non-native, invasive shrubs, such as Eurasian shrub honeysuckle (Lonicera morrowii or L. x bella), Multiflora Rose, Common Buckthorn, Autumn Olive, and Oriental Bittersweet were also quite common in many of the hedges and field edges.

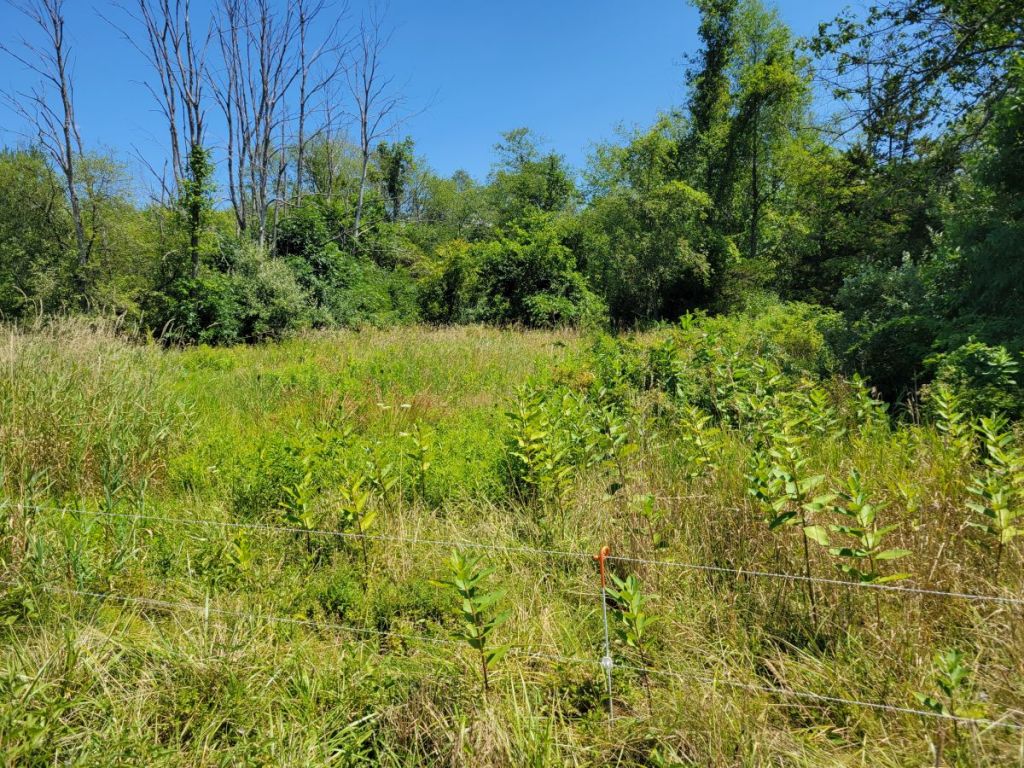
There were a few small wet meadow areas at Churchtown Dairy, such as the one in the next picture at the east end of D6 (#4 on the aerial photograph). These wet meadows support vegetation very different from that in the adjacent upland pastures. European species are also a component of these wet meadows and some, such as the invasive Reed Canary Grass, seen on the left in this image, can be quite common. However, these wet meadows are also important reservoirs of native biodiversity, because they harbor a number of native wildflowers, grasses, sedges, and ferns, which are not found anywhere else on the farm.

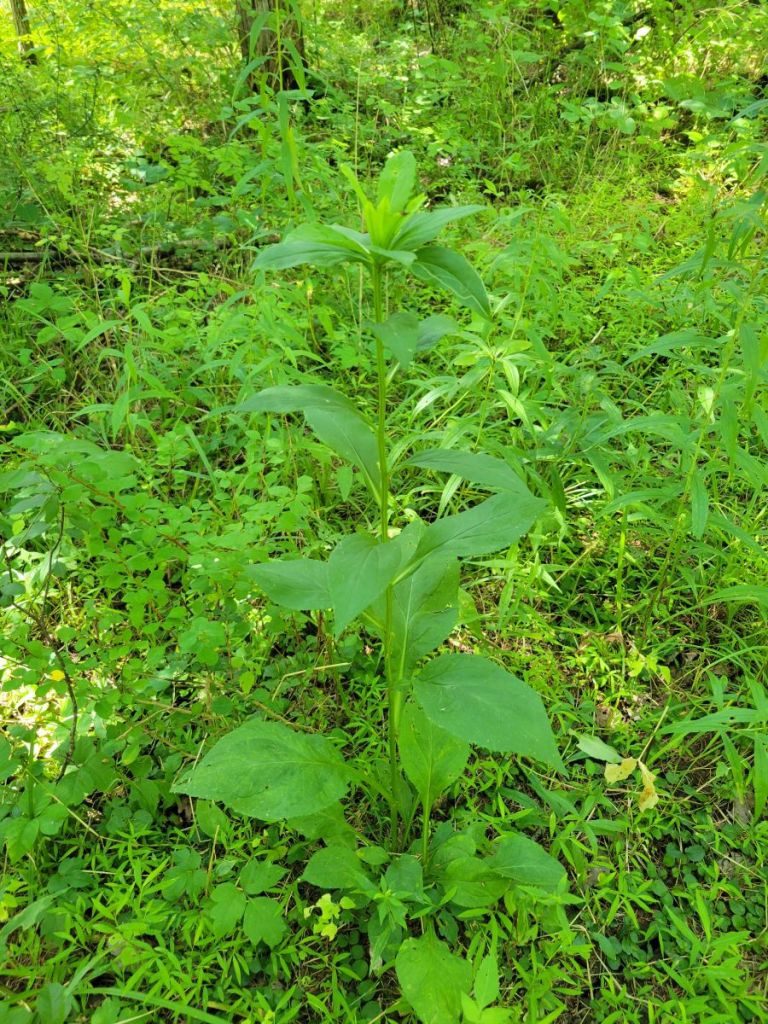
Rough-leaved Goldenrod (Solidago patula) is one example of a regionally uncommon native species I stumbled across in the wet meadow east of D6. This goldenrod, which typically occurs in calcium-rich wetlands, does not grow in dense, rhizomatous colonies like its more common cousins typical of old fields. Instead, a few (eventually) flowering stalks emerge from a cluster of large basal leaves that have the texture of sandpaper.
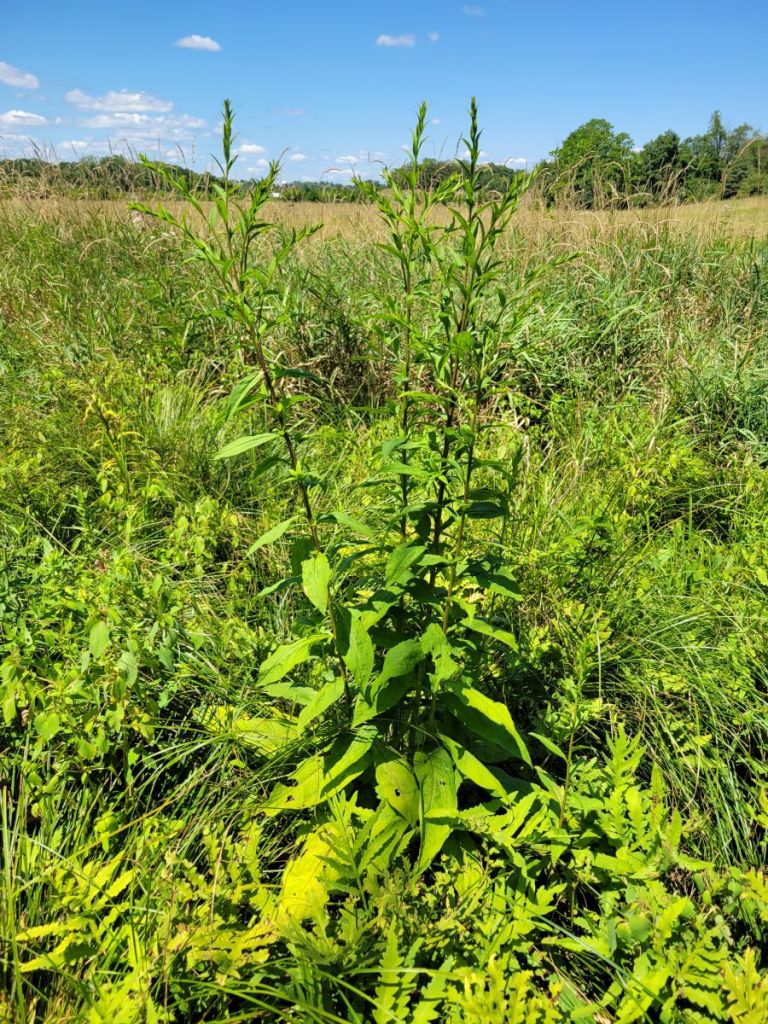

One part of the wet meadow east of D6 supported a colony of Sensitive Fern and cattails (both native species), in addition to a patch of the invasive Reed Canary Grass visible in the front right of the image.

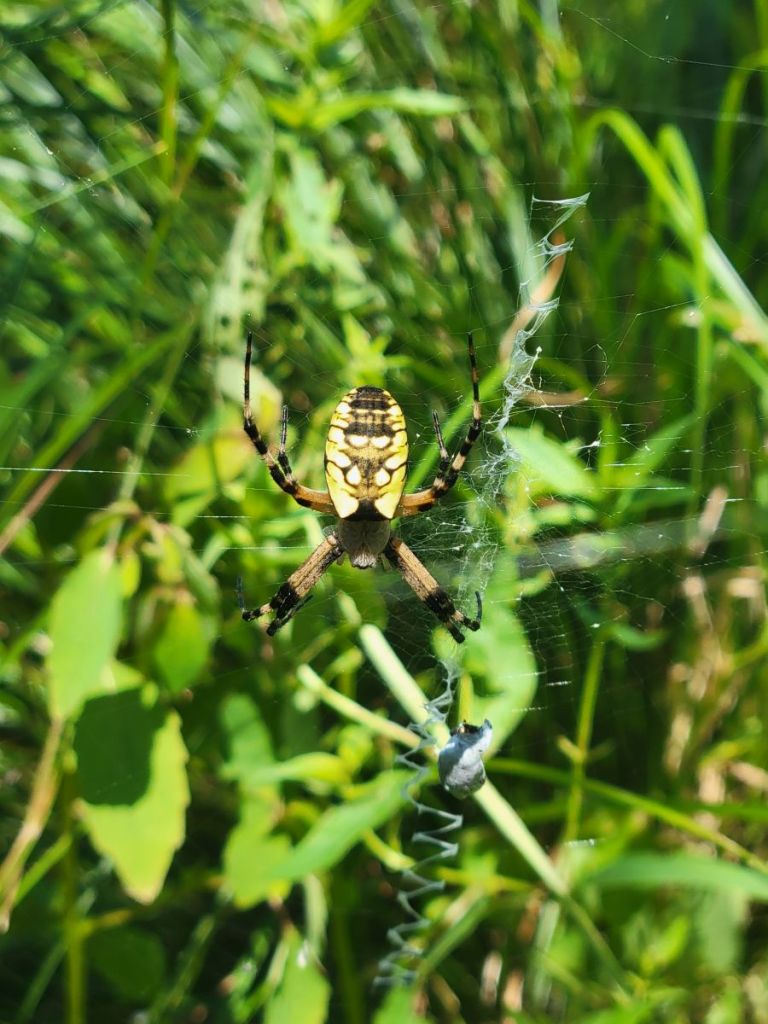
The Black-and-Yellow Gardenspider (Argiope aurantia) builds its net in tall, undisturbed vegetation, and the wet meadow provided ideal habitat for this gorgeous hunter.

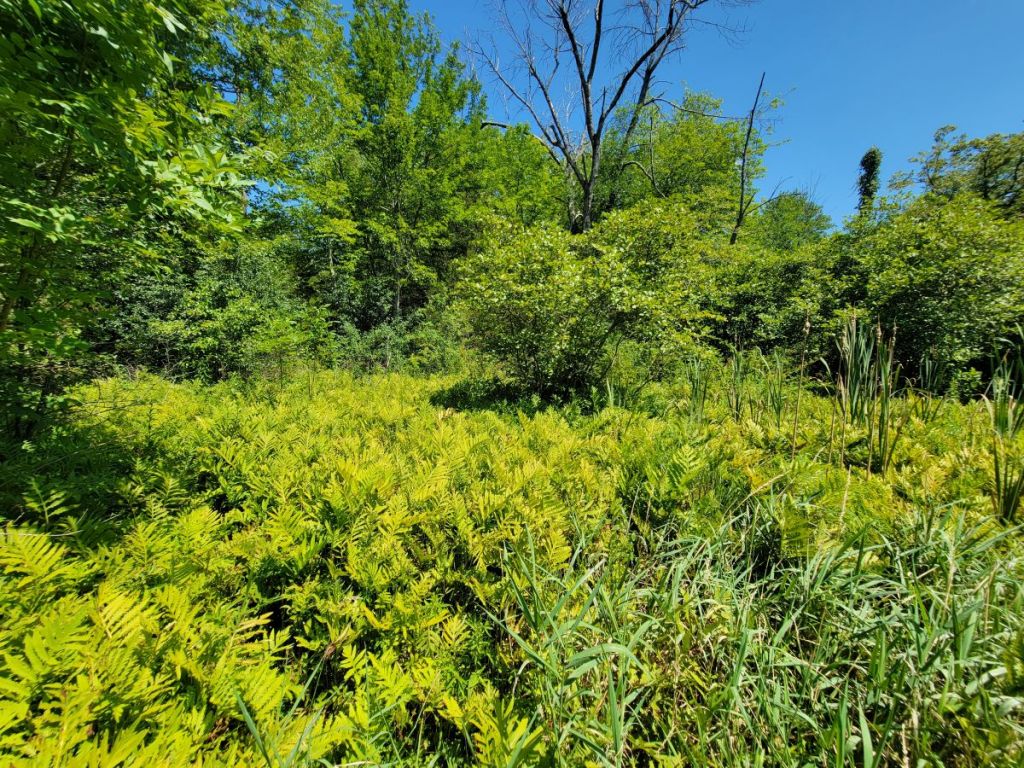
Another beautiful small example of a species-rich wet meadow was found in the drainage southwest of the Bobolink Field (#11). Note the diverse textures and colors in this habitat!

A closer look reveals the native species Woolgrass (Scirpus cyperinus; in front left), Smooth Goldenrod (Solidago gigantea; yellow flowers), Common Boneset (Eupatorium perfoliatum; white flowers), Blue Vervain (Verbena hastata; purple flowers), and Tussock Sedge (Carex stricta; in front right).

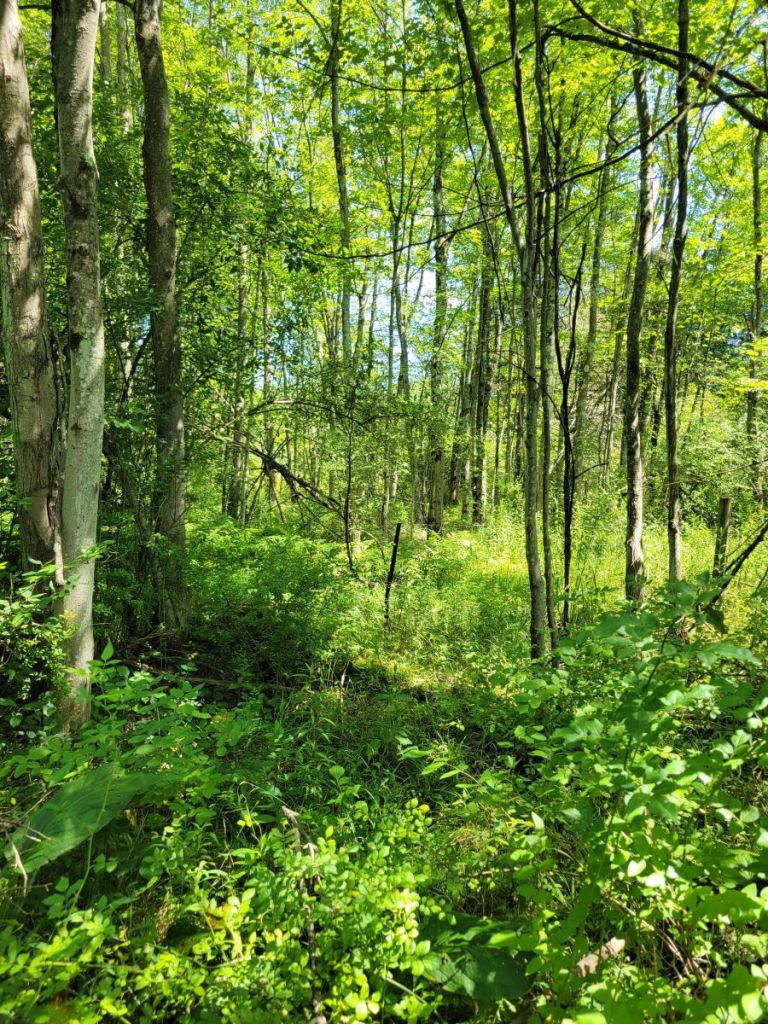
Back at the east edge of D6-11, I entered the forest and found small areas of swamp forest (#5) where the canopy was dominated by Red Maple trees.

Rough-leaved Goldenrod grew here and there in the understory.

Unfortunately, the invasive Japanese Stiltgrass had also established itself in this forest (as well as in the “grove”). This grass is currently one of the most rapidly spreading non-native species in our region and there don’t seem to be any “silver bullets” for its control. It is an annual grass with wiry stems and relatively broad (and short!) leaves, which often have a broad white line along their midrib.

Black Swallowwort (Vincetoxicum nigrum) is an invasive vine with opposite, shiny oval leaves, small, dark purple flowers, and seed pods reminiscent of milkweeds. It was found only in small numbers at Churchtown Dairy. Scattered plants were spotted in the swamp forest and wet meadow east of D6-11, as well as in the “grove.” This might be an invasive species still rare enough on the farm that its spread could be curtailed by systematically pulling it out, whenever it is encountered.

Another potentially troublesome species is this pretty ornamental shrub, Jetbead (Rhodotypos scandens), which probably had jumped the fence onto the young forest on the farm’s land from one of the neighboring yards. I had never seen it growing wild in Columbia County, but was told that it had spread throughout Central Park and might become more assertive in our region, in the future… This might be another species to discourage early on wherever it shows up on the farm.

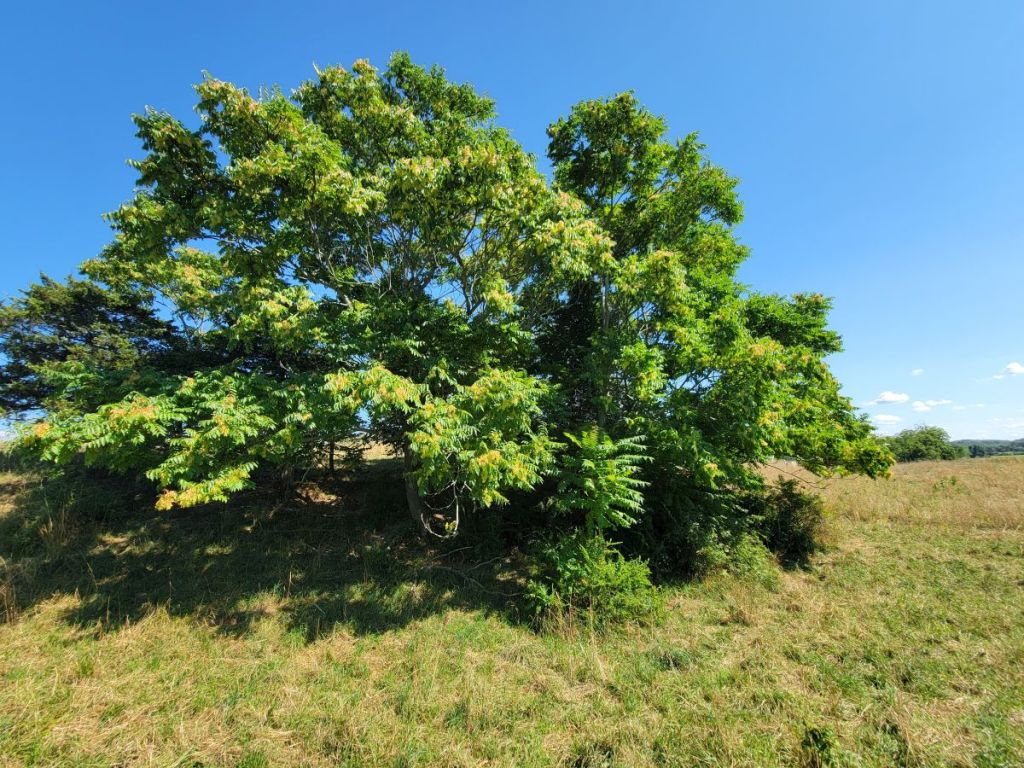
Tree-of-Heaven is the last invasive species I want to mention. It currently occurs at a low enough density at Churchtown Dairy, that its further spread might be avoided by removing the seed-producing trees, like this one next to the “grove.” Unfortunately, if a Tree-of-Heaven is felled, its roots tend to produce sprouts which—if unchecked—can result in an entire colony of new trees. Therefore, it is important to continue to annually monitor and—if needed—manage the site where an adult tree has been felled or girdled.

Returning to the east edge of D6-11, after emerging from the swamp forest, I entered a small stand of Red Cedar trees (#6), which seemed to serve as an occasional forest pasture. I made no exciting native plant discoveries in this habitat.
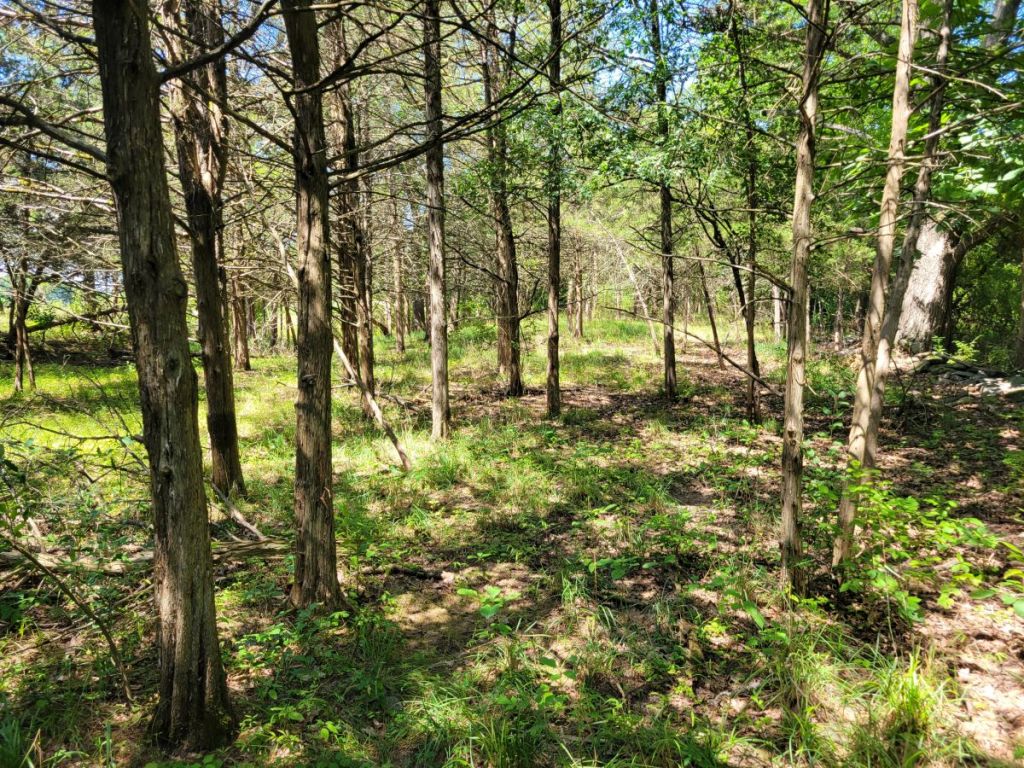

Emerging out of the Red Cedar forest, I found myself on the hilly, eastern section of pasture D11 (#7). Although dry pastures like this sometimes harbor uncommon native plants, I did not observe any noteworthy native species here, either.
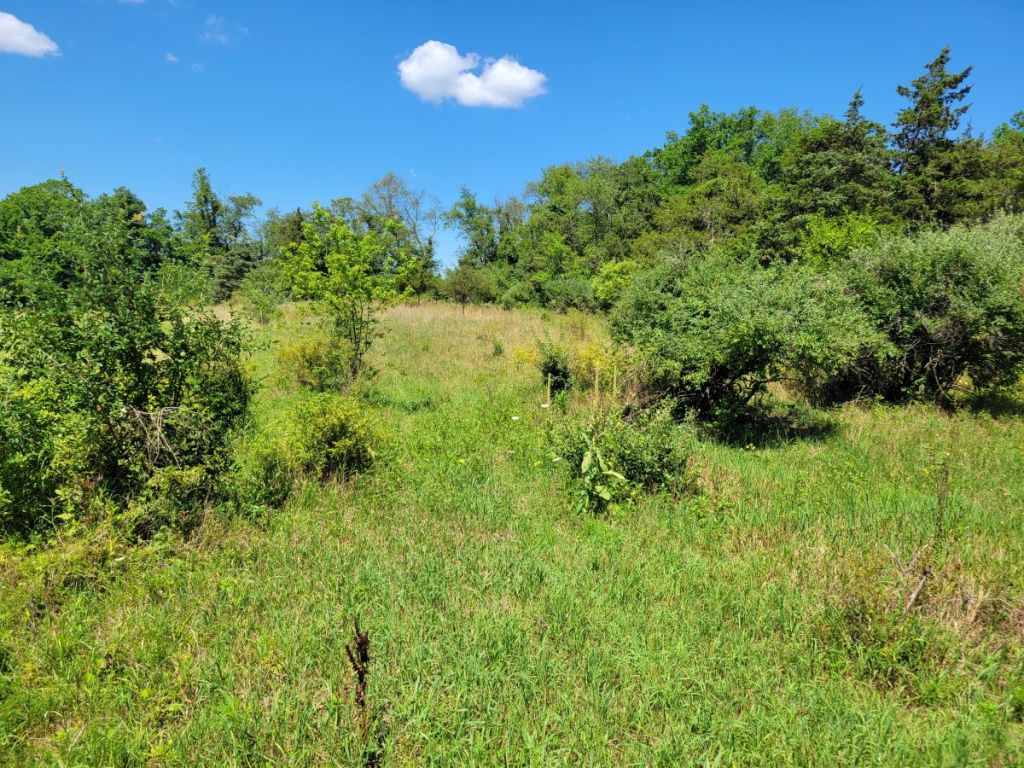

Eventually, I found myself in the “Bobolink Field,” (#12) a hay meadow cut late in the season to give ground-nesting Bobolinks enough time to raise their young. Like in the pastures, the vegetation in this field was mostly composed of European grasses and—to a lesser extent—legumes.
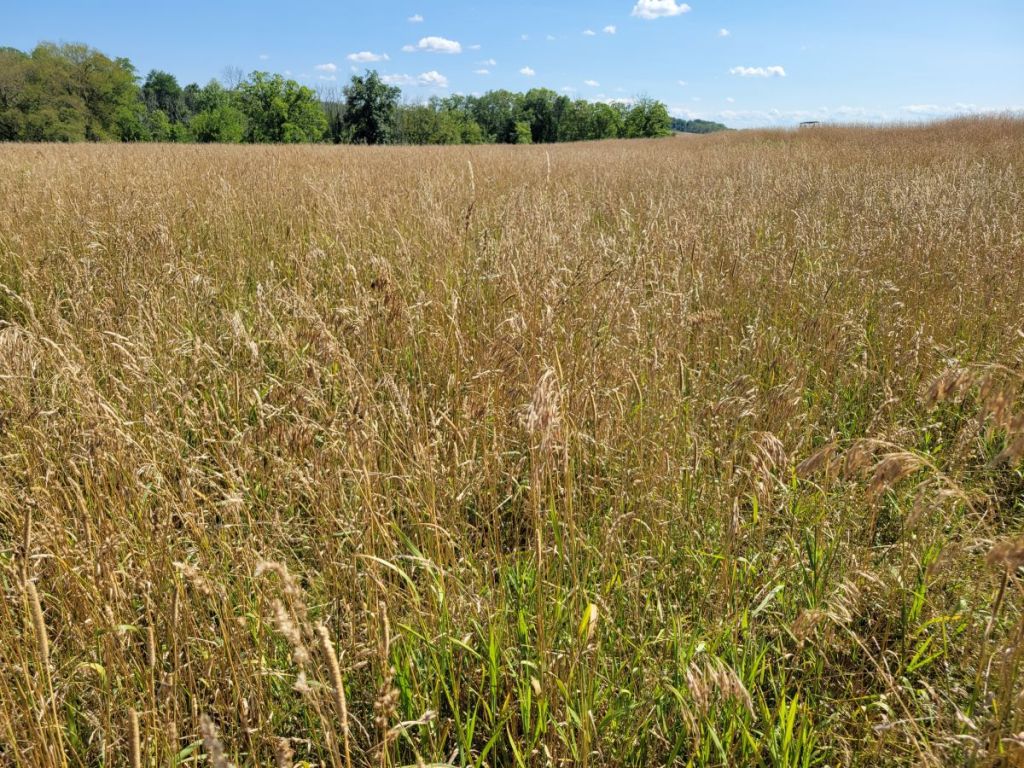

Another wetland, this one dominated by shrubs and trees, including Swamp White Oak, Green Ash (many dying), and Red Maples, borders the “Bobolink Field” on the east. Native shrubs, such as Winterberry, Arrowwood, Silky Dogwood, and Wild Raisin, occur side-by-side with the common invasive shrubs that dominate the understory.

Spotted Joe-Pye-weed grew along the herbaceous edge of this wetland and also in some of the other wet meadows along the eastern edge of the farm.

The “grove” (#13) is the only forest at Churchtown Dairy (at least north of County Route 12) that grows on land that seems to have never been completely cleared. It harbors some exceptionally large specimens of Hop-hornbeam trees and some beautiful White Oaks. At the north end, there are several Common Pear trees and Pignut Hickories. Although hardly an “old-growth” forest, this woodland fits our definition of an “ancient forest,” whose soils have not been homogenized by the plow. Therefore, they might have the potential to support soil life and understory plants that are slow to recolonize post-agricultural forests. However, its current understory vegetation is mostly composed of invasive species and European plants typical of nutrient-enriched barn yards. This is likely due to the recent use of this woodland as a pig pasture.
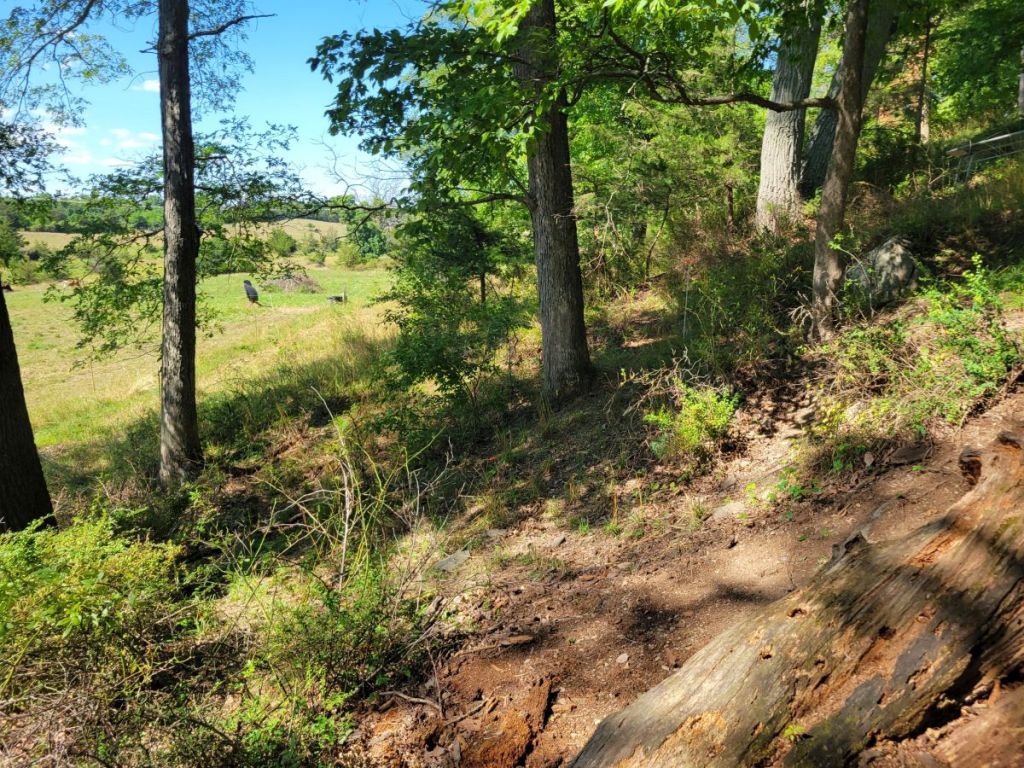

On the way back to the barns, I took a quick detour to this small, marshy pond (#15), which had very little open water. Cattails (tall green vegetation at the center) were growing in a wide band around the shore and were flanked by patches of Reed Canary Grass (tall tan vegetation left and right of the cattails). Closer inspection revealed several native wetland plants we had not noted in the other areas surveyed for plants at Churchtown Dairy that day. They included the regionally common: Water Purslane, Nodding Bur-marigold, and Soft Bulrush.

